Introduction:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has revolutionized medical diagnostics, providing detailed images of the internal structures of the body without the use of harmful radiation. Two common types of MRI machines are the Open MRI and the Closed MRI. In this article, we will delve into the key distinctions between these two technologies and shed light on the duration of an MRI procedure.
Open MRI vs. Closed MRI:
1. Machine Design and Appearance:
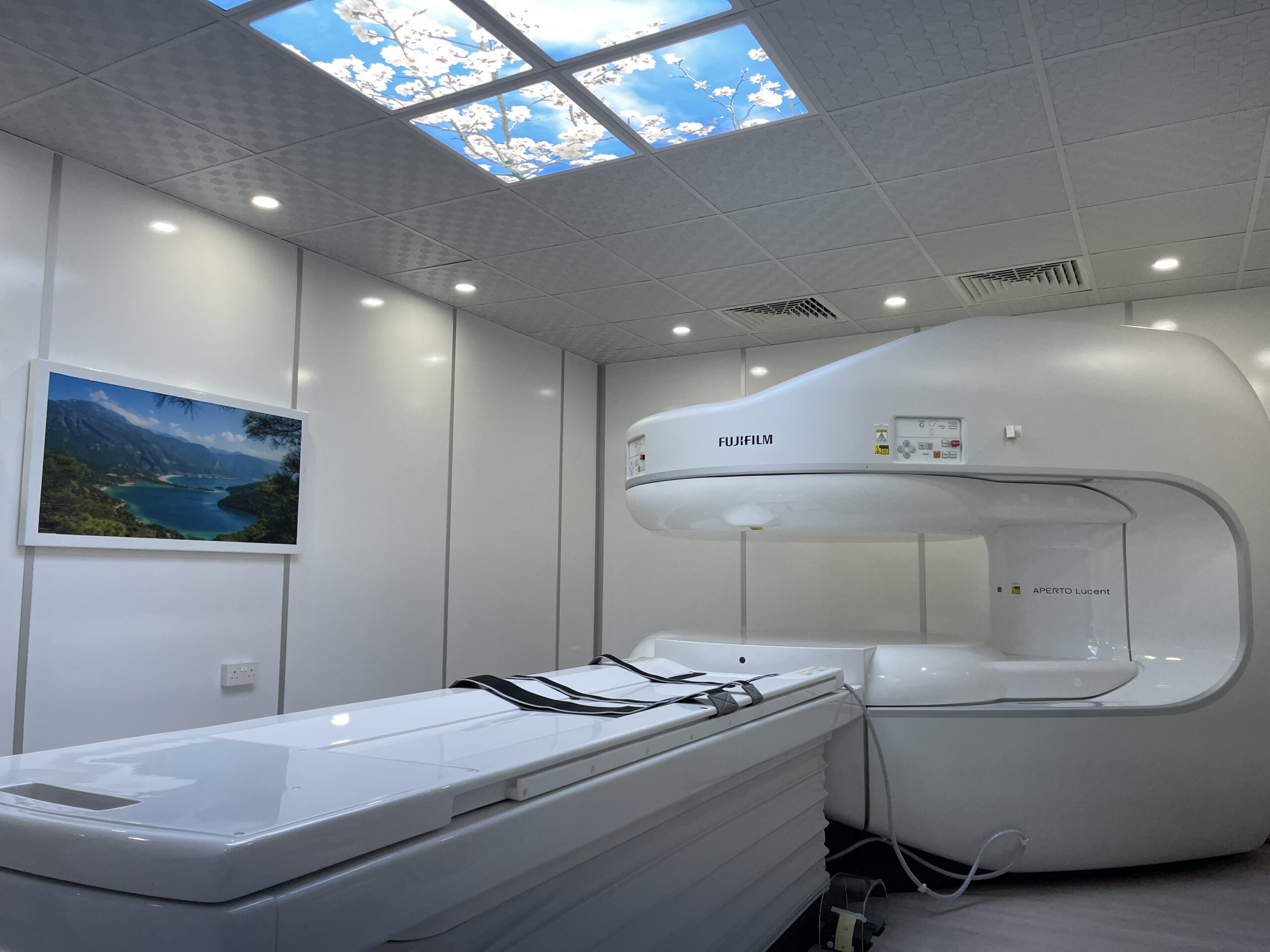
– Open MRI:
– Characterized by a more spacious design with open sides.
– Ideal for patients who may experience claustrophobia or anxiety in confined spaces.
– Suitable for individuals with larger body types.
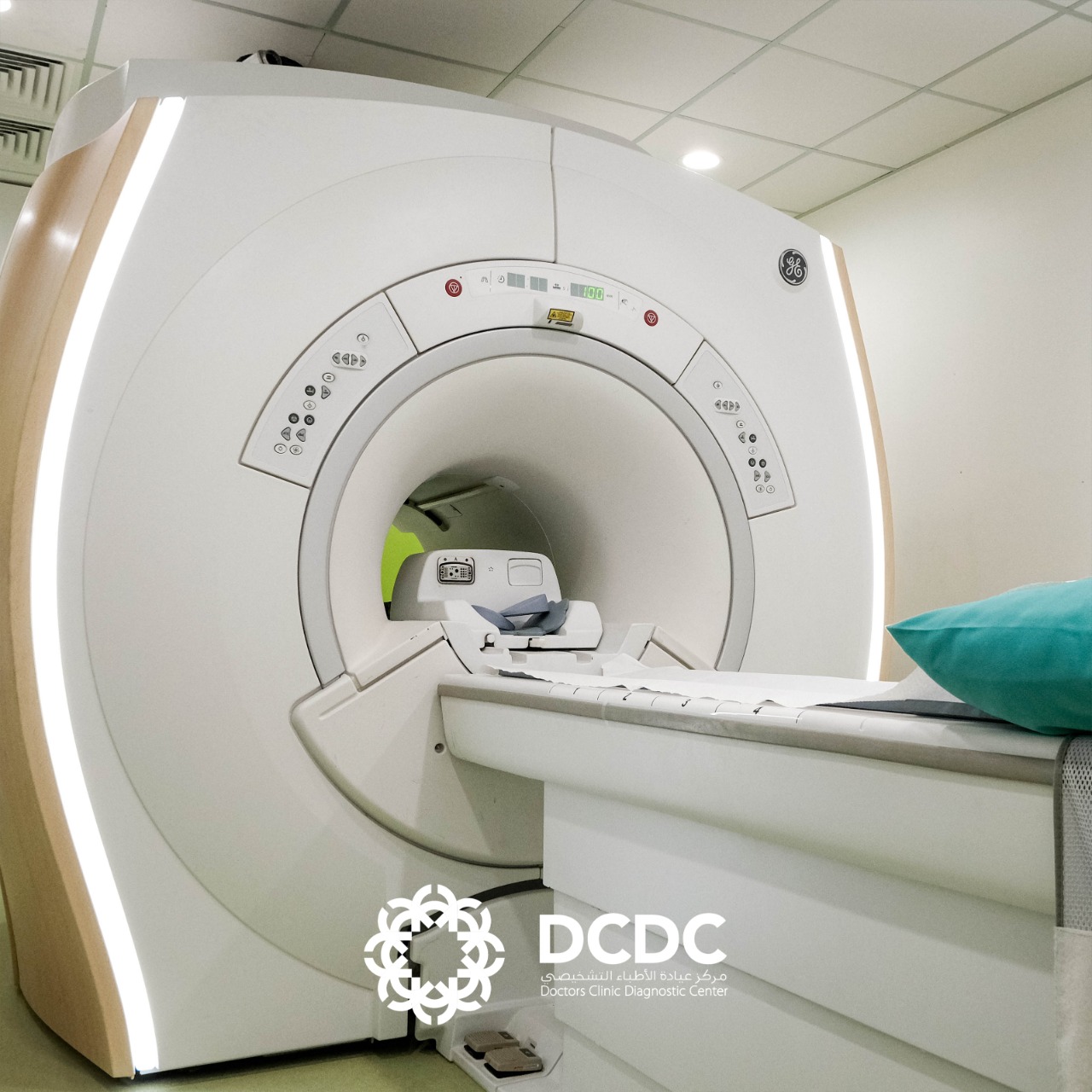
– Closed MRI:
– Features a more tunnel-like structure.
– Can induce feelings of confinement and discomfort, especially for those prone to claustrophobia.
– May be challenging for larger individuals due to its narrower design.
2. Patient Experience:
– Open MRI:
– Generally offers a more comfortable experience for patients.
– Reduces the likelihood of claustrophobia-related stress during the procedure.
– Allows for a more relaxed environment, potentially beneficial for pediatric and anxious patients.
– Closed MRI:
– Some patients may feel confined and anxious during the procedure.
– Claustrophobic individuals may find it challenging to remain still for the required duration.
3. Image Quality:
– Open MRI:
– Historically, open MRI machines were associated with slightly lower image resolution.
– Recent technological advancements have narrowed the gap, with many open MRI systems now providing high-quality images.
– Closed MRI:
– Traditionally associated with higher image resolution.
– Preferred for examinations requiring exceptionally detailed images, such as neurological studies.
4. Procedure Duration:
– The duration of an MRI procedure can vary based on factors such as the body part being examined and the complexity of the imaging required.
– Typically, an MRI takes between 30 and 60 minutes.
– Factors affecting duration include the need for contrast agents, patient cooperation, and the specific imaging protocols.
5. Clinical Applicability:
– Open MRI:
– Well-suited for a variety of imaging needs, especially for larger or claustrophobic patients.
– Used for imaging joints, extremities, and some types of neurological studies.
– Closed MRI:
– Preferred for imaging studies where high resolution and detailed images are crucial, such as brain and spine imaging.
– Widely used in various medical specialties, including neurology, orthopedics, and oncology.
How long does an MRI take?
The duration of an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) procedure can vary based on several factors. Generally, an MRI takes between 30 and 60 minutes, but this can be shorter or longer depending on the specific circumstances. Here are some factors that can influence the length of an MRI:
1. Type of Exam:
– The type of examination being performed greatly influences the duration. For example, a simple study of a single body part may take less time compared to a more complex imaging session involving multiple areas.
2. Body Part Being Examined:
– The part of the body being imaged affects the duration. For instance, imaging a small joint may take less time than scanning the entire spine or brain.
3. Use of Contrast Agents:
– In some cases, a contrast agent (a substance that enhances the visibility of certain tissues or blood vessels) may be injected to improve image quality. This can extend the overall time of the procedure.
4. Patient Cooperation:
– Patient cooperation is crucial for obtaining clear images. Movement during the scan can result in blurry images, necessitating repeated scans and prolonging the procedure.
5. Machine Type:
– The type of MRI machine used can influence the speed of the scan. Some newer machines are designed to acquire images more rapidly than older models.
6. Imaging Protocol:
– The specific imaging protocol prescribed by the healthcare provider can impact the duration. Certain protocols may require more images or longer scanning times to capture detailed information.
7. Patient Comfort and Tolerance:
– The comfort level and tolerance of the patient can also play a role. For individuals who may experience claustrophobia or anxiety, the process may take longer as breaks or additional measures to ensure comfort may be needed.
8. Technologist and Facility Efficiency:
– The experience and efficiency of the MRI technologist, as well as the capabilities of the imaging facility, can affect the overall time of the procedure.
It’s important for individuals scheduled for an MRI to discuss any concerns or potential issues with their healthcare provider or the imaging center beforehand. This can help in making the necessary preparations to ensure a smooth and efficient imaging process. Additionally, understanding the factors that contribute to the duration of an MRI can help manage expectations for the overall experience.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, both Open MRI and Closed MRI play pivotal roles in modern medical imaging. The choice between the two depends on factors such as patient comfort, the body part being examined, and the required image resolution. While Open MRI provides a more comfortable experience for certain patients, Closed MRI remains the gold standard for high-resolution imaging, particularly in critical diagnostic scenarios. The duration of an MRI procedure, regardless of the machine type, generally falls within the 30 to 60-minute range, making it a relatively quick and non-invasive diagnostic tool. As technology continues to advance, both Open and Closed MRI systems are likely to evolve, offering even better imaging quality and patient experiences in the future.