Book Your Appointment
DHA Licensed Specialists
Expert care you can trust
Insurance & Self-Pay
Flexible payment options
Same / Next-Day Appointments
Fast scheduling available
WhatsApp Confirmation
Instant booking updates
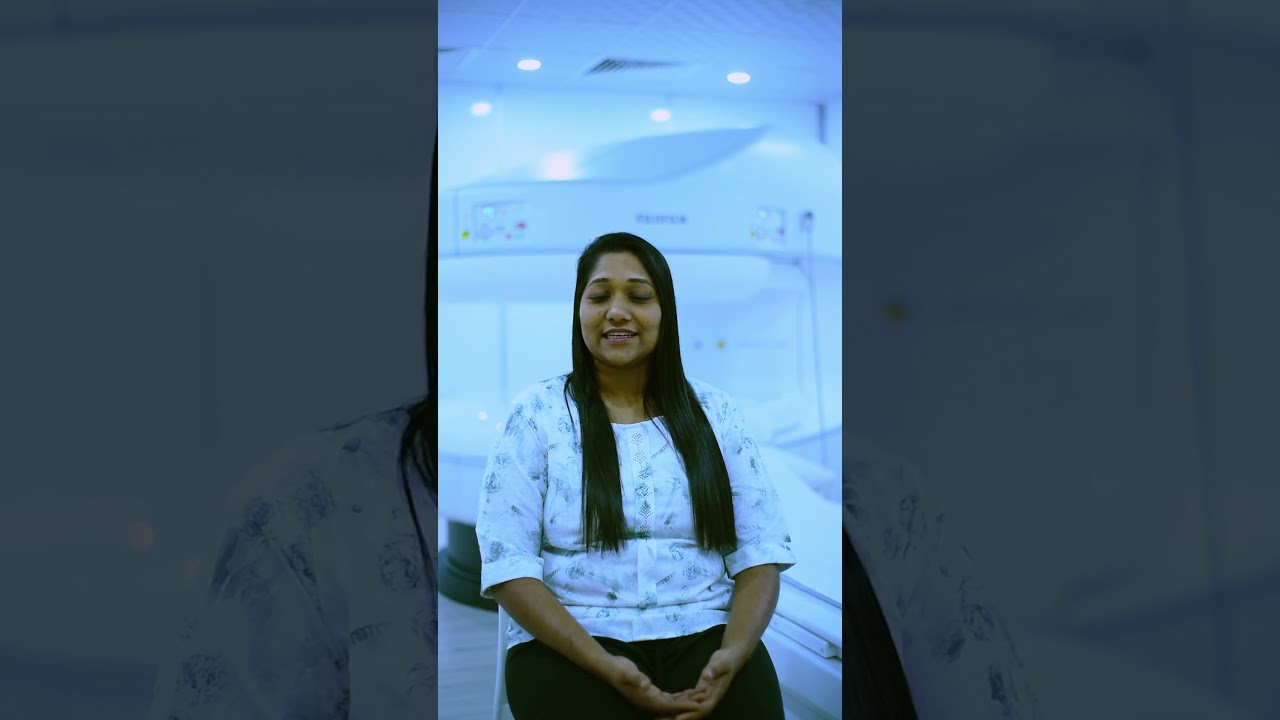
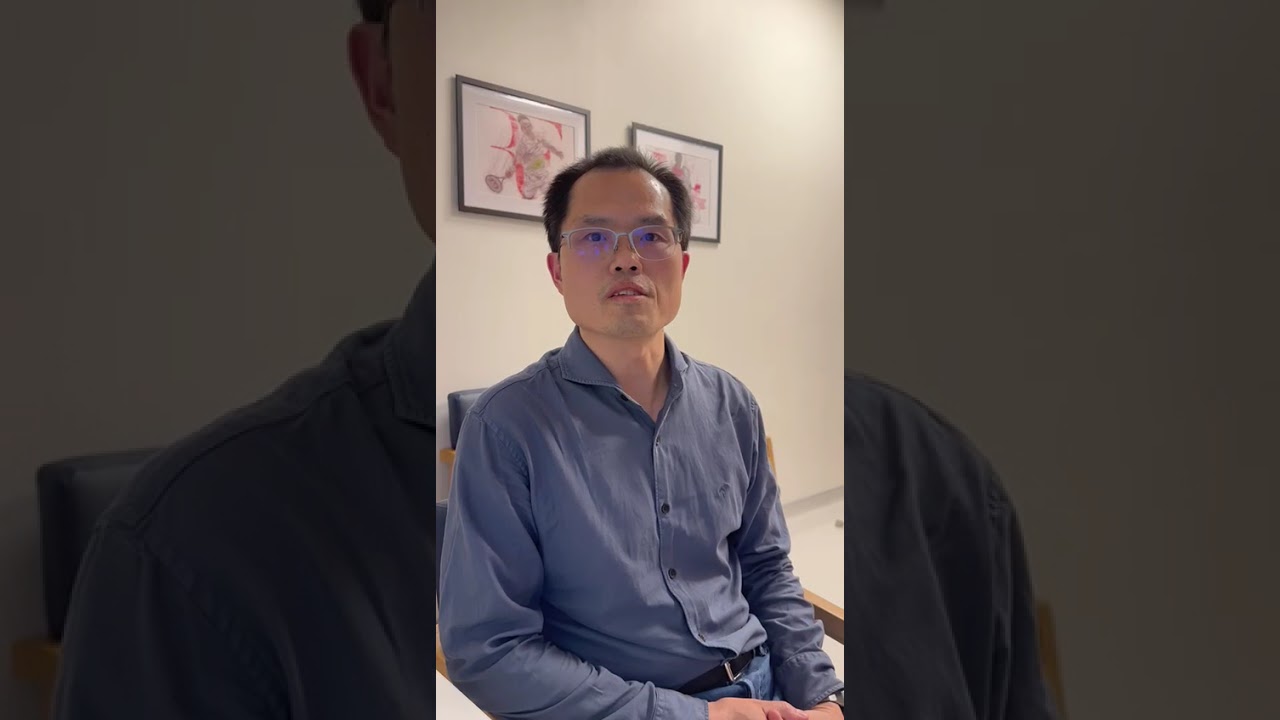
Verified Patient Reviews of DCDC Diagnostic Center in Dubai
Verified reviews and real patient stories from Dubai Healthcare City
I'm very satisfied with this medical clinic. I had my first pregnancy screening here. It was affordable and very professional. The radiologist was welcoming, kind, and made the experience great.
Aizhan Tokmanbetova
Hurt my knee Friday night and got an MRI appointment Sunday evening (booked Sunday afternoon). Waited about 2 minutes and was done in just over 30 minutes. The team was amazing, friendly and efficient.
Kirsten Evans
Dr. Osama's team was gentle and amazing. After a bad experience elsewhere, my pelvic exam here was much more professional. Great report and very precise.
Mary
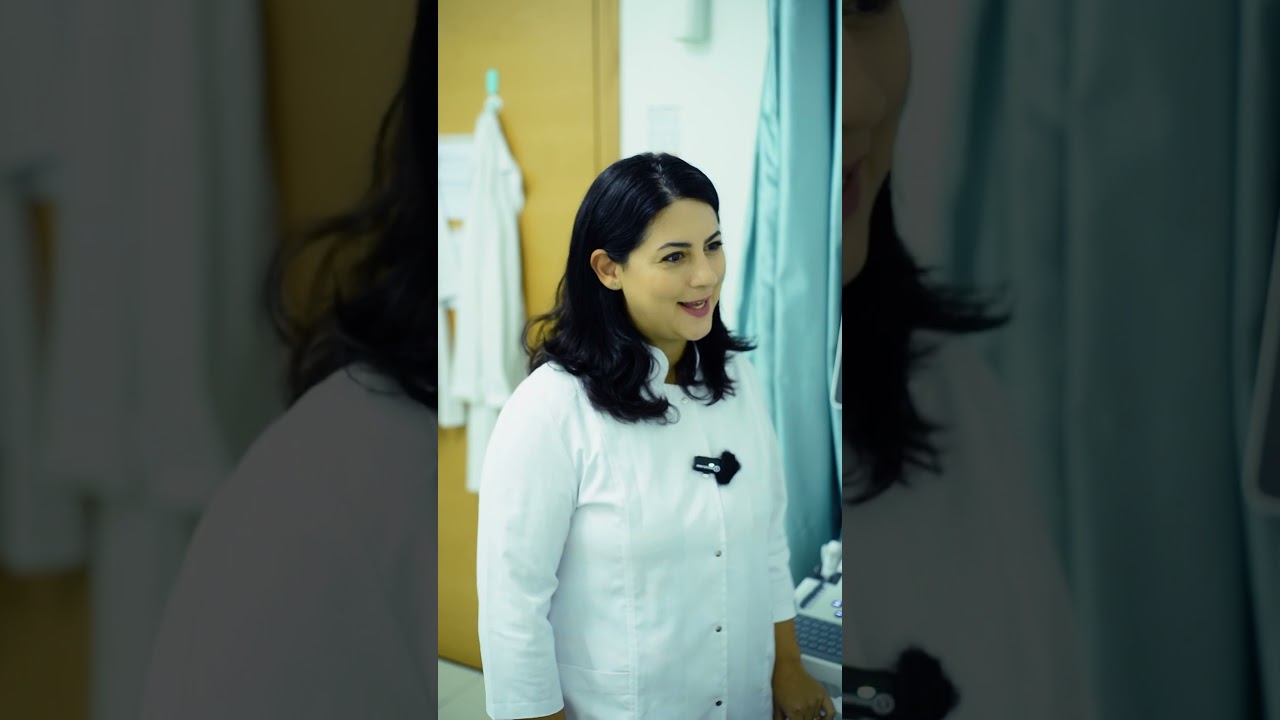



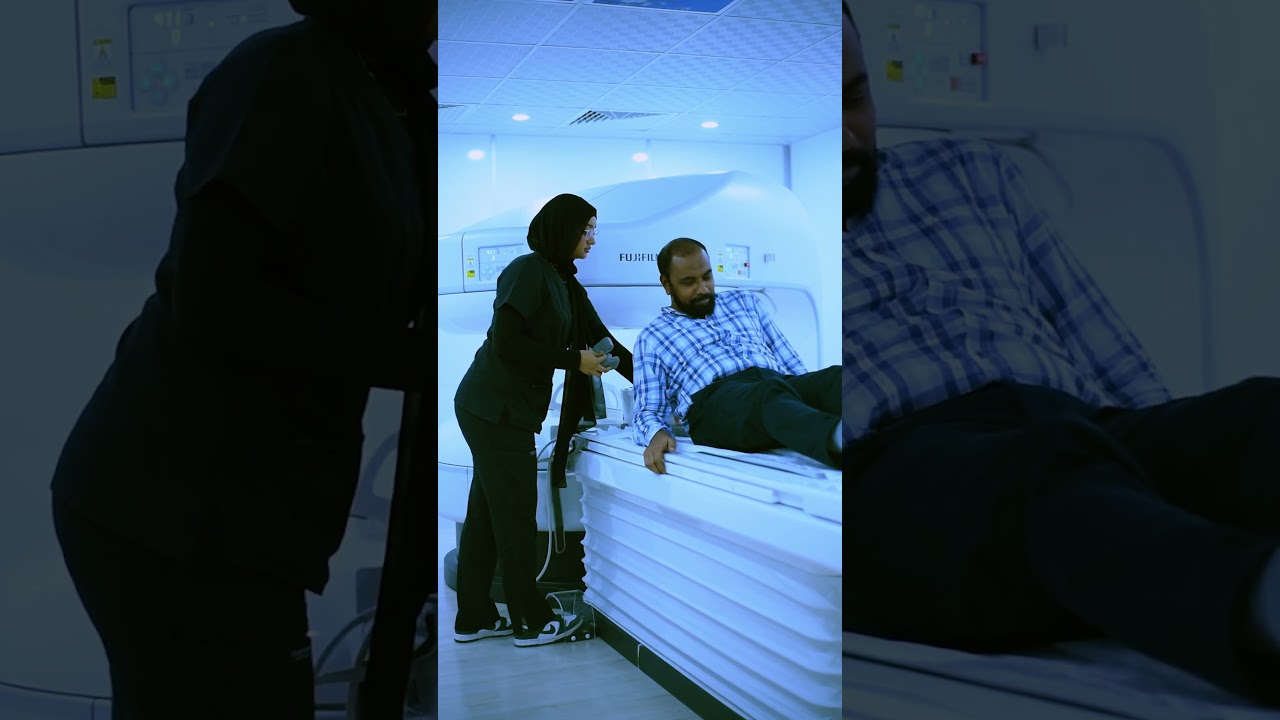
Our Medical Services
Comprehensive healthcare services in Dubai Healthcare City. From advanced diagnostic imaging to specialized consultations, we provide expert care across multiple medical specialties.
DCDC provides medical services in Dubai Healthcare City including diagnostic radiology, cardiology, gynecology & obstetrics, dentistry, orthopedics, and general medicine. Patients visit us from Oud Metha, Downtown Dubai, and across the UAE.
Why Choose DCDC in Dubai Healthcare City?
Accurate diagnostics, experienced specialists, and fast, stress-free appointments in a central Healthcare City location.
Accurate diagnosis you can trust
Advanced diagnostic technology with expert radiologist review for precise results.
Confident treatment decisions
Experienced specialists with international qualifications and years of expertise.
Arabic & English support
Multilingual team ensuring clear communication and comfortable patient experience.
Faster care when it matters
Same-day and next-day appointments available for urgent medical needs.
Approvals & billing handled
Insurance support team helps with pre-authorization and seamless billing.
Easy access in DHCC
Prime location in Dubai Healthcare City with convenient parking and public transport access.
Meet Our Specialists
Experienced medical professionals dedicated to your health and wellbeing
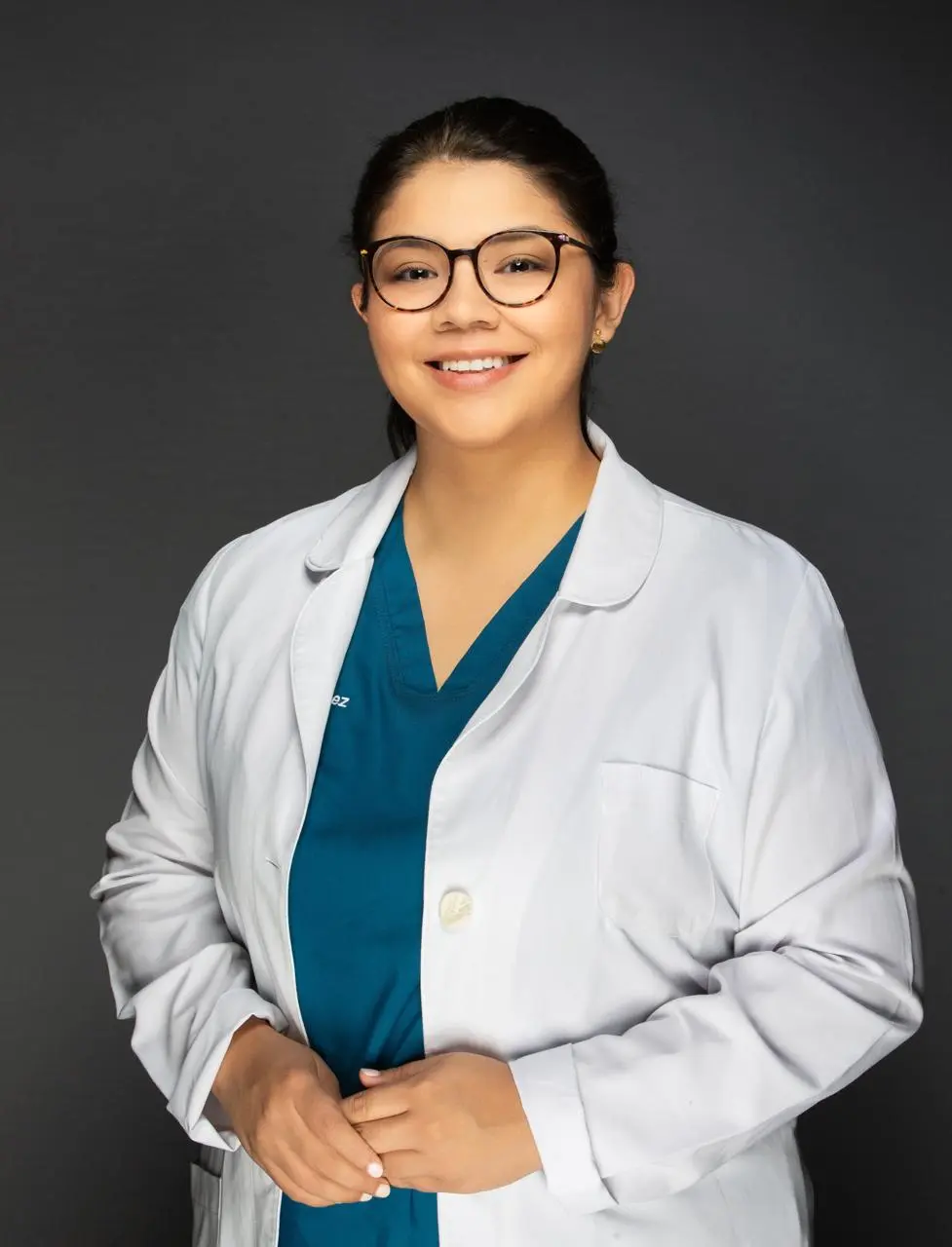

Dr. Maria Ramirez
Gynecology & Obstetrics
Expert in women's health and obstetrics
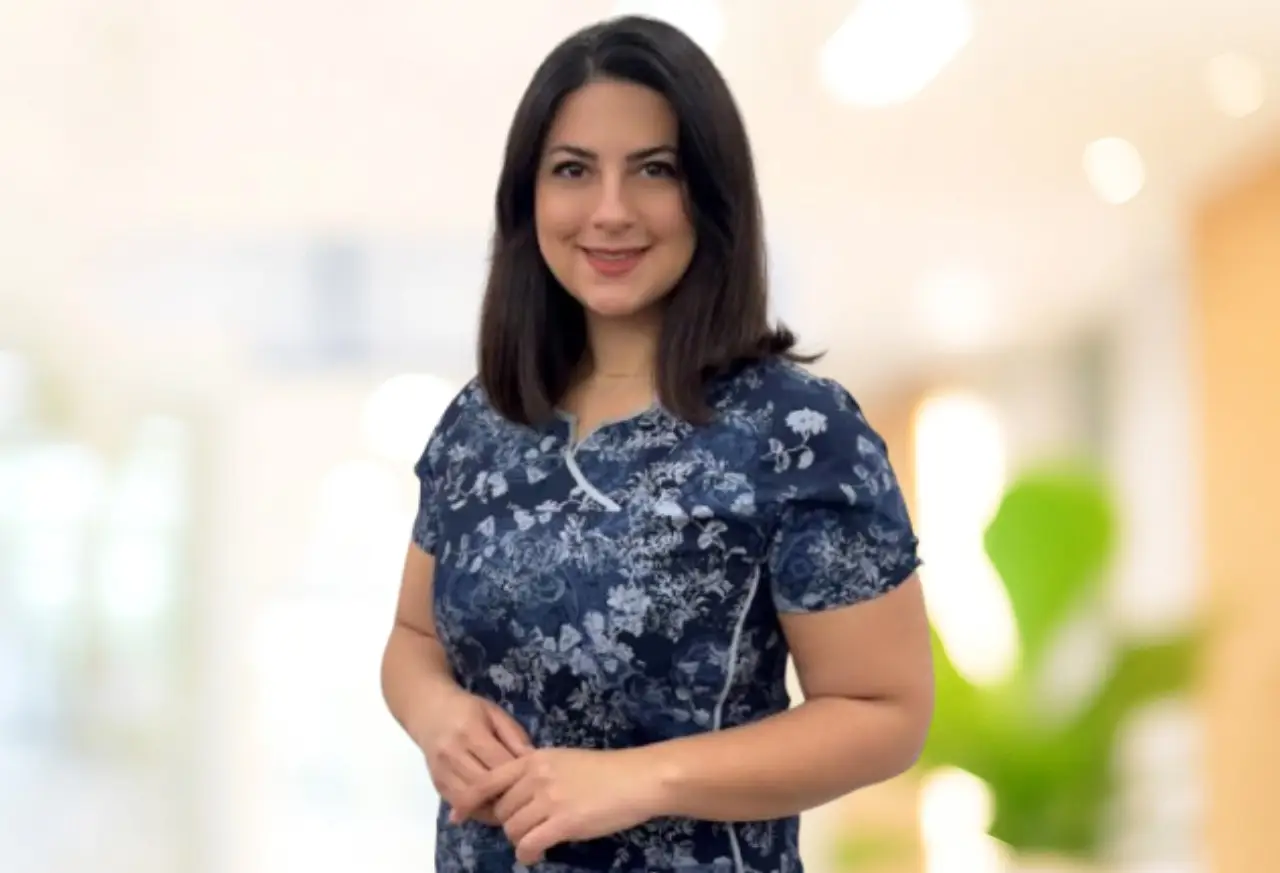

Dr. Parisa Dini
Gynecology & Obstetrics
Expert in women's health and obstetrics
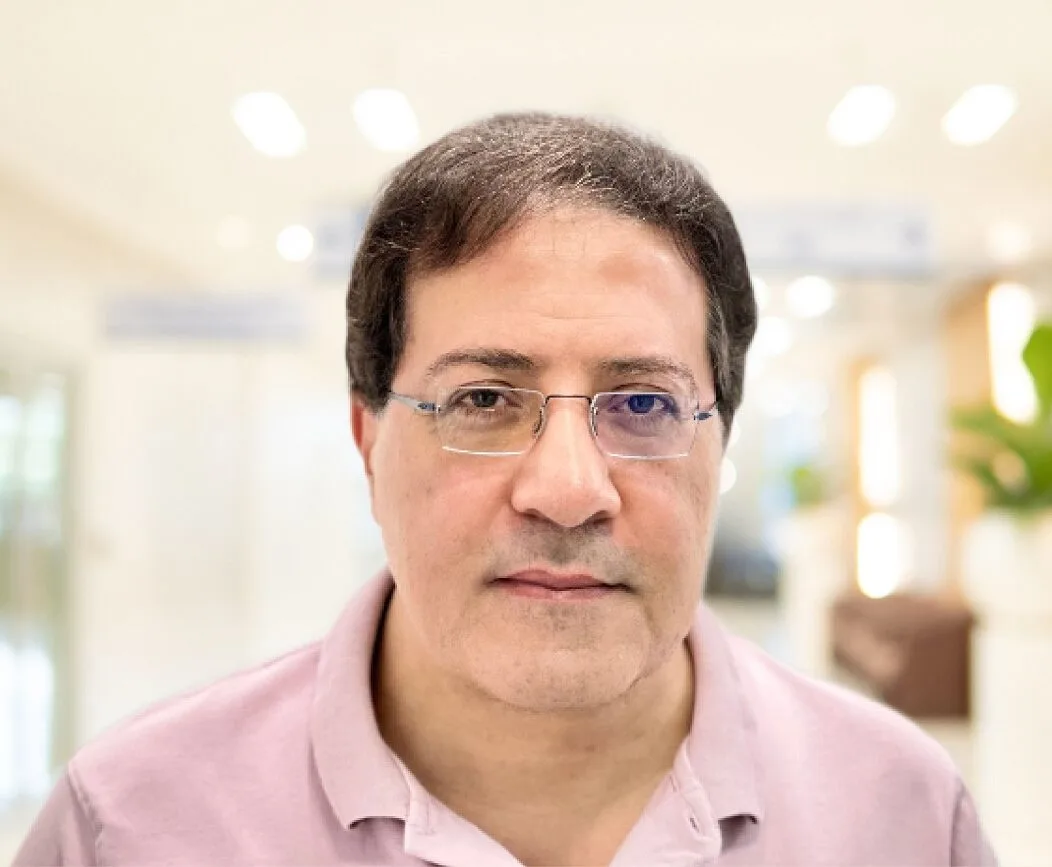

Dr. Osama Elzamzami
Radiology
Expert in diagnostic imaging
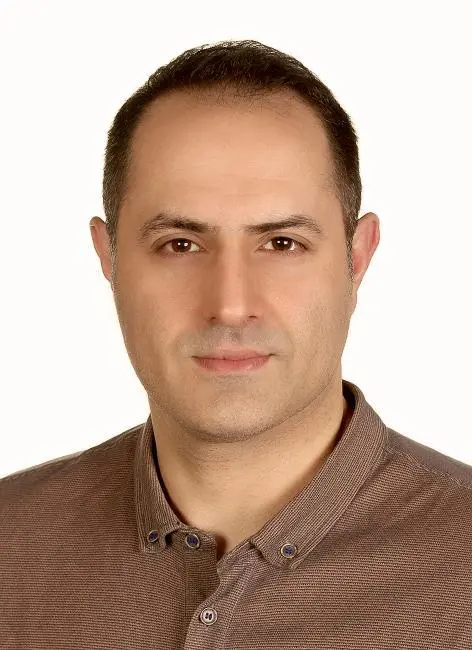

Dr. Mersad Moosavi
Orthopedics
Orthopedic surgery specialist
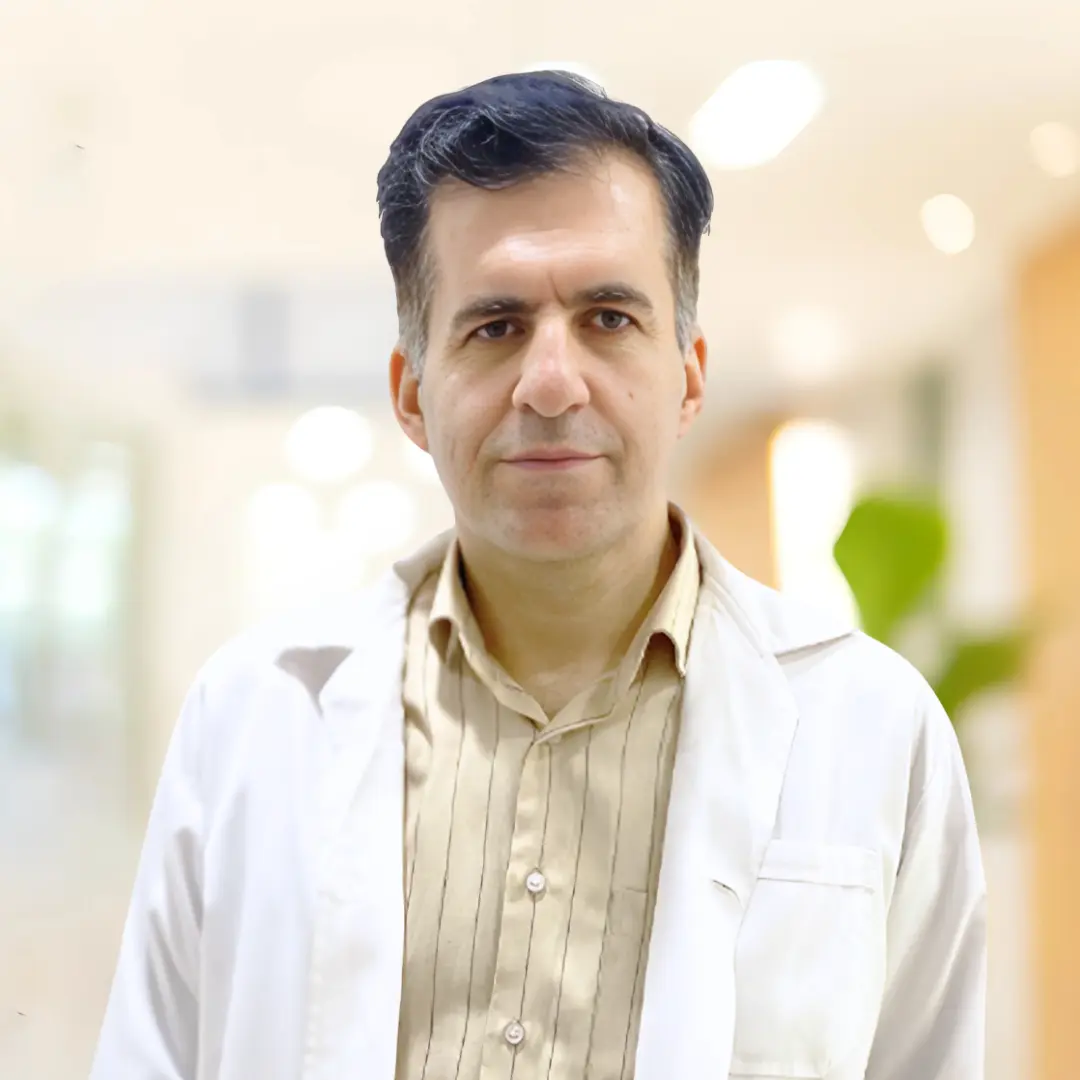

Dr. Shahoo Mazhari
Cardiology
Cardiovascular medicine specialist
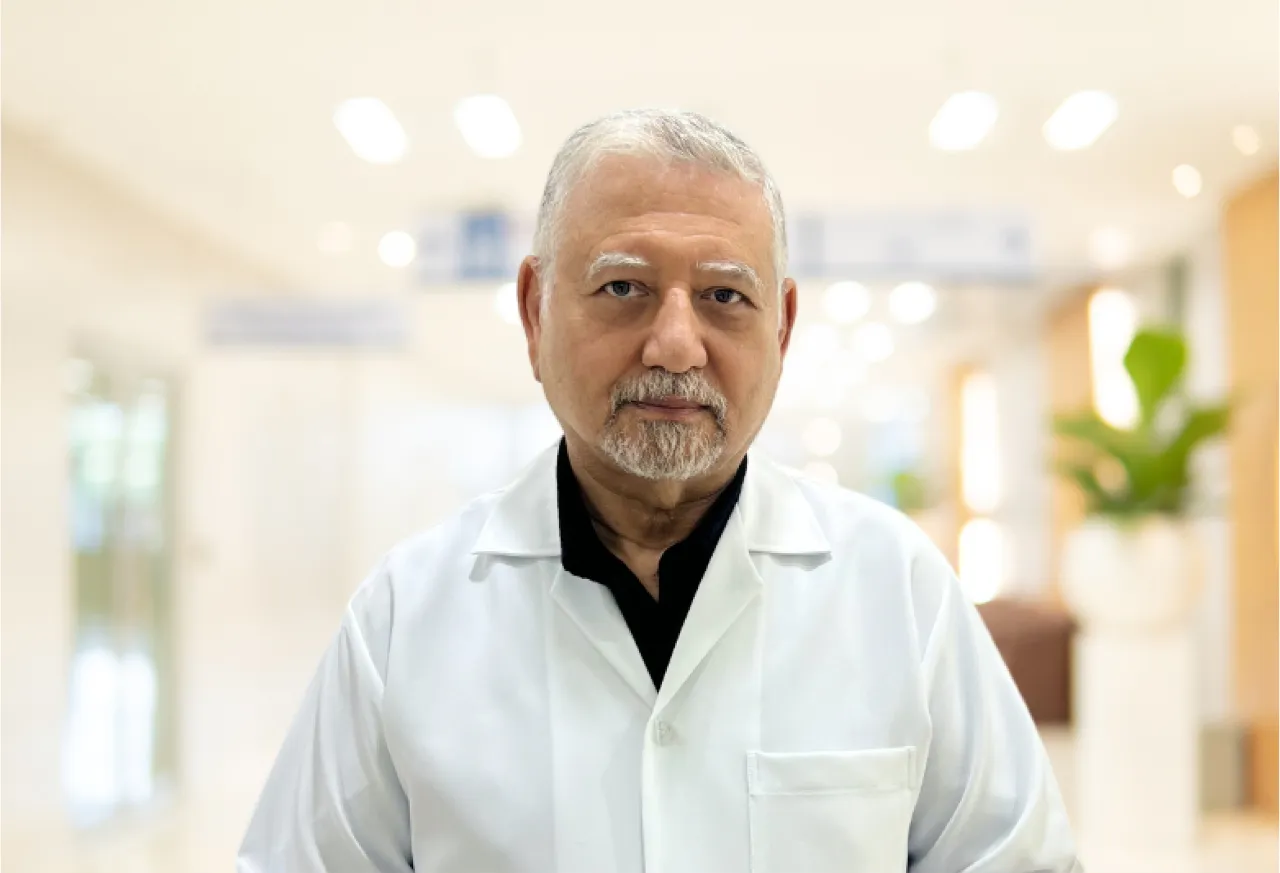

Dr. Riad Trabulsi
Neurology
Neurology specialist
Insurance Partners
We work directly with major insurance providers to make your healthcare experience seamless. Our team handles all approvals to minimize your out-of-pocket costs.
MOHAP License: NIMY7VY5-240925 · Fully licensed medical center in Dubai Healthcare City







And 12 more insurance partners Contact us to verify your coverage.
View All Insurance PartnersVisit Us in Dubai Healthcare City
Conveniently located in the heart of Dubai Healthcare City (DHCC), Building 64, Block A. Easy access from Oud Metha Road, Bur Dubai, Downtown Dubai, Business Bay, Jumeirah, and all major Dubai districts. Free dedicated patient parking available.
Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center
Building 64, Block A, Dubai Healthcare City, Dubai, UAE
Near Oud Metha Road · Free Parking Available
Working Hours
Everyday: 8AM - 10PM | Fri: 10AM - 9PM
Frequently Asked Questions
Everything you need to know about booking and visiting DCDC
Yes, we accept most major insurance providers in Dubai. We work with 20+ insurance companies including Daman, AXA, Bupa, and many others. Our team can help verify your coverage and handle pre-authorization. Self-pay options are also available.
Book Your Appointment Today
Fast confirmation via WhatsApp. Our team will assist you with scheduling and insurance.

