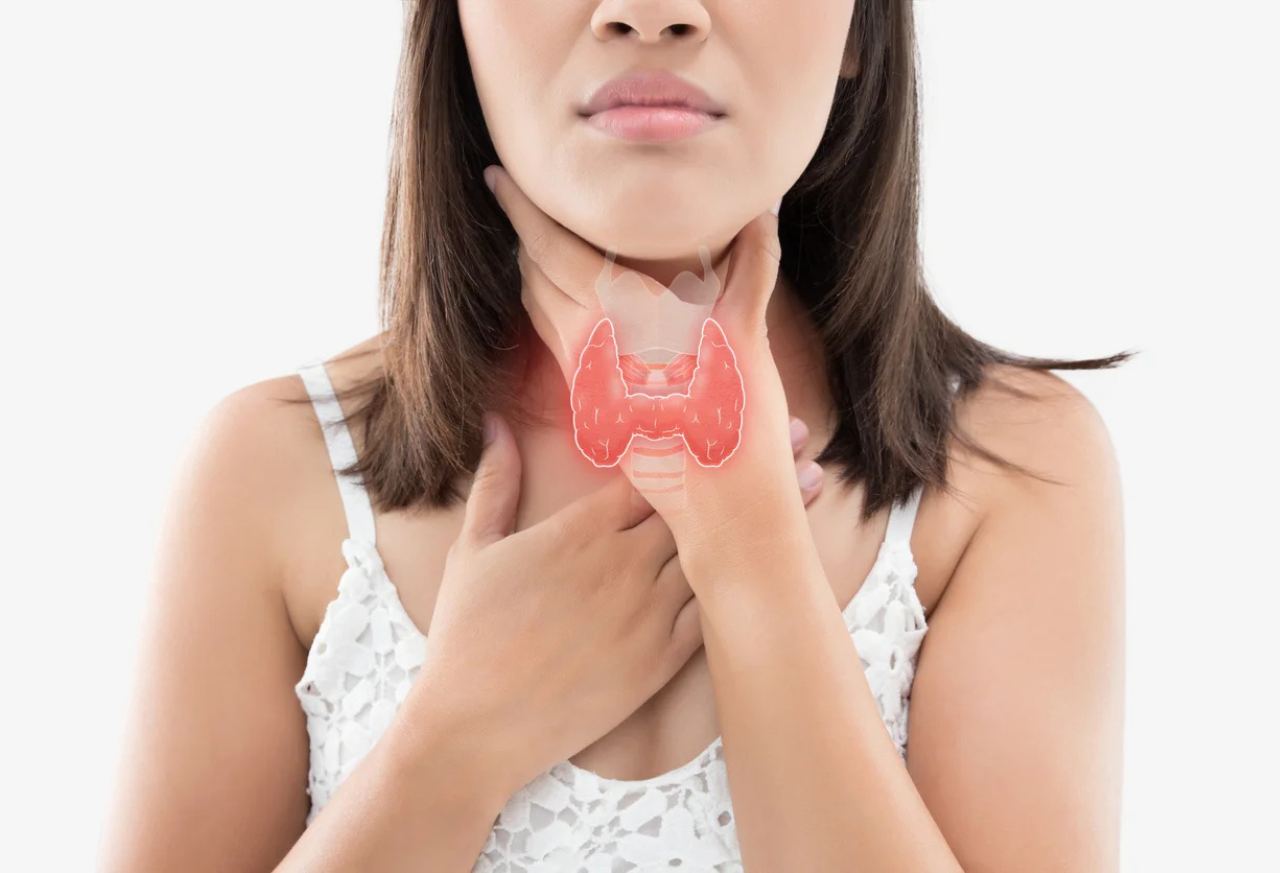
Thyroid disorders encompass a variety of conditions affecting the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ located at the front of the neck. This gland is vital for regulating numerous metabolic processes in the body. Thyroid issues can range from benign, untreated goitres (enlarged glands) to serious, life-threatening cancers. The impact of thyroid disorders can be significant, influencing various bodily functions and leading to severe health complications if left untreated.
Types of Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism: This condition arises when the thyroid gland produces insufficient thyroid hormone, resulting in a slowdown of bodily functions. Causes include Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, hyperthyroidism treatments, radiation therapy, and certain medications.
Hyperthyroidism: In contrast, hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces excessive thyroid hormone, accelerating bodily functions. It can be caused by Graves’ disease, thyroid nodules, and thyroiditis.
Goitre: A goitre is an enlargement of the thyroid gland and can occur in both hypo- and hyperthyroidism. It may also result from iodine deficiency.
Thyroid Nodules: These lumps in the thyroid gland are usually benign, though a small percentage can be cancerous.
Thyroid Cancer: Less common but serious, thyroid cancer can develop in the thyroid gland cells, often presenting as a nodule or lump.
Gender Disparities and Age of Onset
Thyroid disorders are more common in women than men, influenced by female-specific physiological and life stages such as pregnancy and menopause, as well as a higher incidence of autoimmune conditions. Despite this gender disparity, men are also at risk and can experience symptoms that significantly affect their health. Both genders can suffer systemic effects from thyroid dysfunction, impacting metabolism, cardiovascular health, and emotional well-being.
Thyroid disease can affect all ages, from infants to the elderly. It can be congenital or develop later, often post-menopause in women. Around 20 million Americans have some form of thyroid disorder, with women being five to eight times more likely to be affected than men.
Risk Factors
– Family history of thyroid problems
– Autoimmune diseases like Type 1 diabetes, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis
– High iodine medication use, such as amiodarone
– Age over 60, especially in women
– Previous thyroid treatments or cancer
Diabetes and Thyroid Disorders
Having diabetes, particularly Type 1, increases the risk of thyroid disorders. Regular screening for thyroid issues is crucial for individuals with diabetes, with Type 1 diabetes patients being tested annually. Proper management includes adequate sleep, regular exercise, dietary adjustments, and adherence to medication regimens for both conditions.
Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism Symptoms:
– Fatigue
– Weight gain
– Cold intolerance
– Constipation
– Dry skin
– Hair loss
– Slow heart rate
– Muscle weakness
– High cholesterol
– Depression
– Memory impairment
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms:
– Weight loss
– Heat intolerance
– Increased appetite
– Anxiety
– Rapid heartbeat
– Tremors
– Sweating
– Menstrual changes
– Light sensitivity
– Sleep difficulties
Thyroid Nodules and Cancer Symptoms:
– Neck lump
– Swallowing difficulty
– Breathing difficulty
– Hoarseness
Health Implications
Thyroid disorders can profoundly affect various bodily systems due to the thyroid gland’s role in regulating metabolism and energy. Hypothyroidism can lead to heart disease, peripheral neuropathy, and fertility issues. Hyperthyroidism can cause heart palpitations, atrial fibrillation, and thyrotoxic crisis. Thyroid cancer, though rare, poses significant risks if not detected early.
Role of an Endocrinologist
Consulting an endocrinologist, a specialist in hormone and gland disorders, is essential if you experience thyroid symptoms or if tests indicate thyroid issues. They use blood tests, imaging, and other diagnostic tools to develop personalised treatment plans, which may include medication, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery. Continuous monitoring ensures effective management of the condition.
Management of Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism: Treated with synthetic thyroid hormone replacement.
Hyperthyroidism: Managed with medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery.
Goiter and Nodules: May require surgery if symptomatic or cancerous.
Thyroid Cancer: Treated with surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, and thyroid hormone therapy.
Effective management with medical care, particularly from endocrinologists, enables most people with thyroid disorders to lead healthy lives. Regular check-ups and adherence to treatment plans are crucial.
At the Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center in Dubai Healthcare City, our Endocrinology Department offers comprehensive care for thyroid disorders. Our team uses advanced diagnostics and evidence-based treatments to ensure the best outcomes. We provide a supportive environment, addressing both the physical and emotional challenges of thyroid disorders. Learn more about our services and support at the Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center’s Endocrinology department.