Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern healthcare, technological advancements have played a pivotal role in revolutionizing diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Among these innovations, ultrasound technology stands out as a versatile and non-invasive tool that has transformed the way healthcare professionals gather crucial information about the human body. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the role of ultrasound in contemporary healthcare, exploring its applications, benefits, and the ongoing advancements in this field.
The Basics of Ultrasound Technology
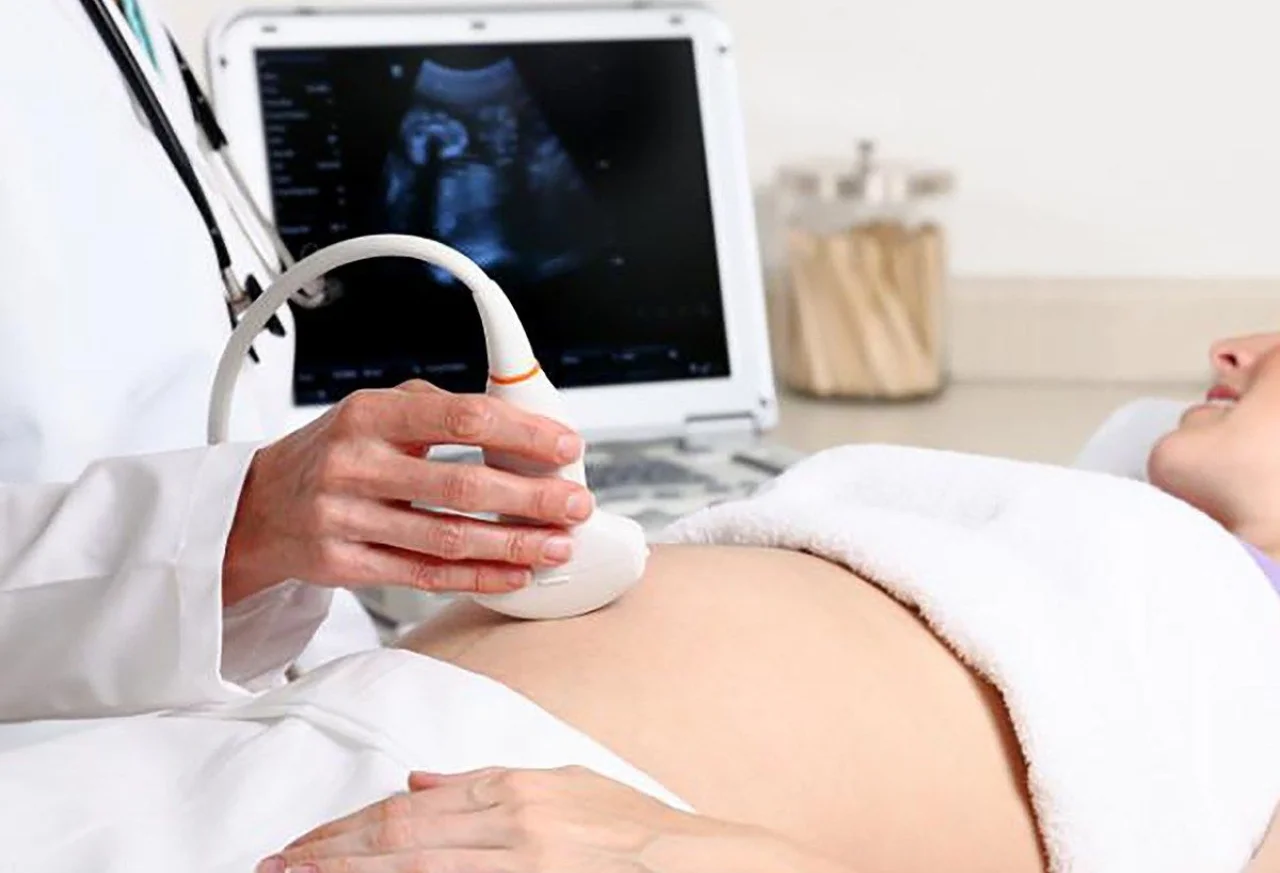
Ultrasound, also known as sonography, utilizes high-frequency sound waves to generate images of the internal structures of the body. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, ultrasound imaging does not involve ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for both patients and healthcare providers. The basic principle involves the transmission of sound waves into the body, with the echoes creating detailed images that help visualize organs, tissues, and blood flow.
Diagnostic Applications of Ultrasound
1. Obstetrics and Gynecology
One of the most well-known applications of ultrasound is in obstetrics, where it allows healthcare professionals to monitor fetal development, detect abnormalities, and ensure a healthy pregnancy. In gynecology, ultrasound aids in diagnosing conditions such as ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, and endometriosis.
2. Cardiology
Ultrasound plays a crucial role in assessing the structure and function of the heart. Echocardiography, a specialized ultrasound technique, helps in diagnosing heart conditions, evaluating blood flow, and assessing the overall cardiac performance.
3. Abdominal Imaging
Ultrasound is widely used to examine abdominal organs, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys. It assists in identifying abnormalities such as tumors, cysts, or stones.
4. Musculoskeletal Imaging
In sports medicine and orthopedics, ultrasound helps visualize muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints. This is valuable for diagnosing injuries, guiding injections, and monitoring rehabilitation progress.
5. Emergency Medicine
Portable ultrasound devices have become invaluable in emergency situations, allowing quick assessments of trauma victims, identification of fluid accumulation, and aiding in various critical care scenarios.
Benefits of Ultrasound in Healthcare
1. Non-Invasiveness
Unlike certain imaging techniques that require injections or exposure to ionizing radiation, ultrasound is entirely non-invasive. This reduces the risk of complications and makes it a preferred choice for various patient populations.
2. Real-time Imaging
Ultrasound provides real-time imaging, enabling healthcare professionals to observe moving structures, such as a beating heart or a developing fetus. This dynamic aspect is particularly beneficial in guiding interventional procedures.
3. Portability and Accessibility
Advances in technology have led to the development of portable ultrasound devices, expanding their use in point-of-care settings. This portability enhances accessibility, especially in resource-limited or remote areas.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to some imaging modalities, ultrasound is generally more cost-effective. This affordability contributes to its widespread use and accessibility in various healthcare settings.
Recent Technological Advancements
1. 3D and 4D Imaging
Traditional 2D ultrasound images have been enhanced with the introduction of 3D and 4D imaging. These technologies provide a more detailed and realistic representation of anatomical structures, improving diagnostic accuracy and patient understanding.
2. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS)
Contrast agents can be used to enhance the visibility of blood flow and tissue perfusion during ultrasound examinations. CEUS has proven valuable in assessing vascular conditions, liver lesions, and other areas where increased contrast is beneficial.
3. Elastography
This technique measures tissue stiffness, aiding in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis, breast lesions, and prostate conditions. Elastography adds a functional dimension to ultrasound, providing valuable information about tissue elasticity.
Challenges and Future Directions
While ultrasound has undoubtedly revolutionized healthcare, there are still challenges and areas for improvement. One limitation is the operator-dependence of the technique, as obtaining high-quality images requires skill and experience. Ongoing research focuses on automating image acquisition and analysis, potentially reducing this dependency.
Future directions in ultrasound technology include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) for image interpretation and the development of miniaturized, wearable devices. These innovations aim to further enhance the efficiency, accessibility, and diagnostic capabilities of ultrasound in healthcare.
Conclusion
Ultrasound technology has become an indispensable tool in modern healthcare, with applications spanning various medical specialties. Its non-invasiveness, real-time imaging capabilities, and cost-effectiveness make it a preferred choice for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. As technology continues to advance, ultrasound’s role is likely to expand, contributing to improved patient care, enhanced diagnostic accuracy, and increased accessibility to healthcare services. Understanding the fundamentals and ongoing developments in ultrasound is crucial for healthcare professionals and patients alike as they navigate the ever-evolving landscape of modern medicine.