Introduction
In the realm of medical diagnostics, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has emerged as a powerful tool, providing detailed insights into the human body’s inner workings. This article delves into the intricacies of how an MRI scan is performed, shedding light on its principles, applications, and the overall experience for the patient.
Principles of MRI Imaging
Understanding the foundation of MRI is crucial. It operates on the principles of magnetic resonance and radiofrequency signals. When a patient enters the MRI machine, the body’s atoms align with a powerful magnetic field. Subsequent radiofrequency pulses stimulate these atoms, producing signals that are translated into detailed images by the machine’s sophisticated technology.
Types of MRI Scans
MRI scans are versatile, serving various medical purposes. Structural MRI captures detailed images of organs and tissues, while Functional MRI (fMRI) observes brain activity. Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) focuses on blood vessels, providing vital information for cardiovascular assessments.
Preparing for an MRI Scan
Before undergoing an MRI, patients are typically advised to adhere to certain guidelines. This includes dietary restrictions and removing metallic objects, as any interference could impact the accuracy of the scan.
What to Expect During the Procedure
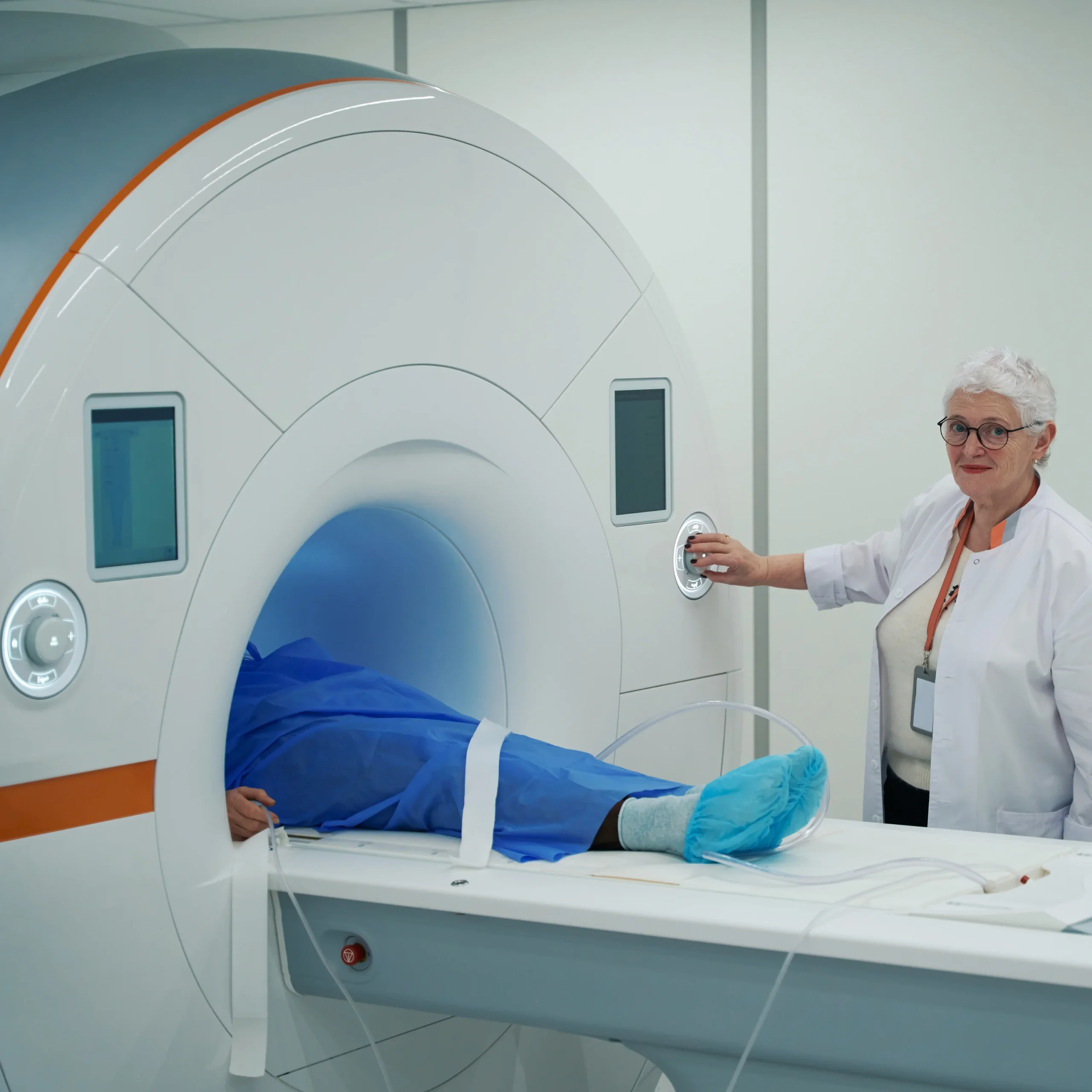
Once inside the MRI machine, patients need to remain still for the duration of the scan. The process is painless, though some may find the enclosed space of the machine challenging. However, advancements in open MRI designs cater to those with claustrophobia concerns.
Benefits of MRI Scans
One of the primary advantages of MRI scans is their non-invasiveness. Unlike surgical procedures, MRI provides high-resolution images without any incisions, aiding in precise diagnoses.
Limitations and Considerations
While MRI scans are highly valuable, there are limitations to consider. Patients with certain implants or devices may be restricted from undergoing an MRI. Claustrophobia remains a common concern, prompting the need for open MRI alternatives.
Applications in Various Medical Fields
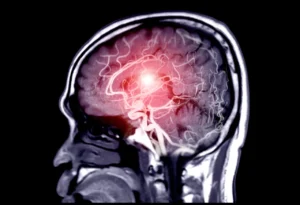
MRI’s applications span across medical specialties. In neurology, it assists in identifying brain abnormalities, while orthopedics relies on MRI for detailed views of musculoskeletal structures. In oncology, MRI aids in cancer detection and treatment planning.
Innovation in MRI Technology
Technological advancements continue to enhance MRI capabilities. Advanced imaging techniques, such as diffusion-weighted imaging and spectroscopy, provide more comprehensive insights. Contrast agents further improve visibility, especially in soft tissue areas.
Comparisons with Other Imaging Techniques
In comparison to CT scans and X-rays, MRI stands out for its ability to offer detailed, three-dimensional images without ionizing radiation. This makes it a preferred choice for certain diagnostic scenarios.
Post-Scan Follow-Up
After the scan, patients consult with a radiologist to interpret the results. This step is crucial for understanding any potential health concerns and determining the appropriate course of action.
Safety Measures and Concerns
Certain safety measures are in place, particularly for pregnant individuals. While MRI is generally safe, the potential risks and considerations are discussed with patients before the procedure.
Cost and Accessibility of MRI Scans
The accessibility of MRI scans may vary based on geographical locations and healthcare systems. Understanding insurance coverage is vital for patients to manage the potential costs associated with these scans.
Patient Experiences and Testimonials
Real-life stories from individuals who have undergone MRI scans can help demystify the process. Addressing common fears and misconceptions contributes to a more informed and comfortable patient experience.
Future Trends in MRI Technology
The future of MRI technology holds exciting possibilities. Integration with artificial intelligence promises more efficient and accurate diagnoses. Miniaturization of MRI machines could potentially make this diagnostic tool more widely available.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an MRI scan is a remarkable diagnostic tool that has revolutionized medical imaging. Its non-invasive nature, coupled with high-resolution imaging, makes it indispensable in various medical fields. As technology continues to evolve, the future of MRI holds promises of even more advanced and accessible diagnostic capabilities.
FAQs
1. Is an MRI scan safe during pregnancy?
Ans – Yes, in most cases, MRI scans are considered safe during pregnancy. However, precautions are taken, and the procedure is usually avoided during the first trimester.
2. How long does an MRI scan take?
Ans – The duration of an MRI scan varies depending on the type and complexity of the imaging required. It can range from 15 minutes to over an hour.
3. Are there alternatives to traditional closed MRI machines?
Ans – Yes, open MRI machines are available for individuals who experience claustrophobia or anxiety in enclosed spaces.
4. What happens if I move during an MRI scan?
Ans – Remaining still during an MRI scan is crucial for accurate imaging. If you move, the images may be blurred, and the scan may need to be repeated.
5. Are MRI scans covered by insurance?
Ans – Many insurance plans cover the cost of medically necessary MRI scans, but coverage may vary. It’s advisable to check with your insurance provider beforehand.