Ключевые выводы
- Renal Doppler ultrasound evaluates blood flow to and within the kidneys using sound waves
- It is the primary non-invasive test for detecting renal artery stenosis, a leading cause of secondary hypertension
- The test plays a critical role in monitoring transplanted kidneys for rejection and vascular complications
- Patients with resistant hypertension, unexplained kidney function decline, or diabetes benefit most from renal Doppler
- The scan requires 6-8 hours of fasting and takes approximately 20-30 minutes
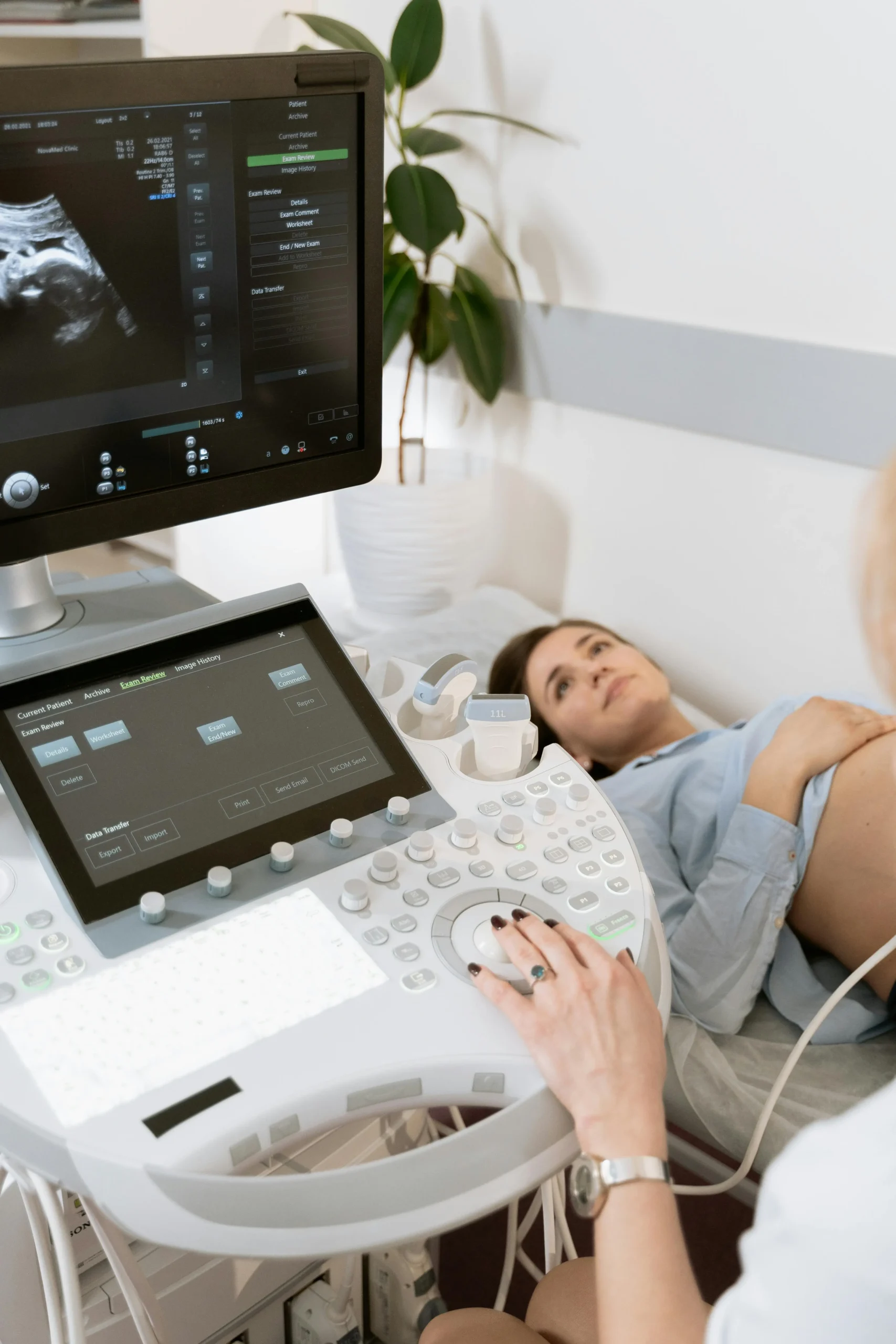
A renal Doppler ultrasound is a specialized imaging test that evaluates blood flow through the renal arteries and veins, providing detailed information about how well blood reaches and circulates within the kidneys. This non-invasive scan is essential for detecting conditions that affect kidney blood supply, including renal artery stenosis, and plays a vital role in monitoring patients with transplanted kidneys, resistant hypertension, and chronic kidney disease.
What Is a Renal Doppler Ultrasound?
A renal Doppler ultrasound combines standard ultrasound imaging with Doppler flow analysis to evaluate the blood vessels that supply the kidneys. While a regular kidney ultrasound shows the size, shape, and structure of the kidneys, a Doppler study adds the critical dimension of blood flow measurement. It can detect narrowing, blockages, or abnormal flow patterns in the renal arteries and veins that standard imaging cannot identify.
The test measures several important parameters including peak systolic velocity (PSV) in the renal arteries, the renal-to-aortic ratio (RAR), and the resistive index (RI) within the kidney itself. These measurements help physicians determine whether the kidneys are receiving adequate blood flow and whether any vascular abnormalities are present.
What Does a Renal Doppler Reveal?
A renal Doppler ultrasound can detect and evaluate several important conditions affecting kidney vascular health. Understanding what this test reveals helps patients appreciate its diagnostic value.
Renal Artery Stenosis
Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is a narrowing of one or both arteries that supply the kidneys with blood. It is one of the most common causes of secondary hypertension, meaning high blood pressure caused by an identifiable underlying condition rather than primary hypertension. RAS is most often caused by atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in the arteries) in older adults or fibromuscular dysplasia in younger women.
During a renal Doppler, stenosis is identified by increased blood flow velocity at the site of narrowing. A peak systolic velocity greater than 200 cm/s in the renal artery, or a renal-to-aortic ratio greater than 3.5, strongly suggests significant stenosis. The test can also detect complete occlusion where no flow is present, which helps guide urgent treatment decisions.
Kidney Transplant Monitoring
For patients who have received a kidney transplant, renal Doppler is one of the most important monitoring tools. The test can detect vascular complications of transplantation including renal artery stenosis at the surgical connection site, renal vein thrombosis, and arteriovenous fistulas. Changes in the resistive index within the transplanted kidney can also signal early rejection before clinical symptoms appear.
Transplant recipients typically undergo renal Doppler assessment within the first few days after surgery, then at regular intervals during the first year and beyond. Any sudden decline in kidney function prompts an immediate Doppler evaluation to rule out vascular causes.
Kidney Blood Flow Assessment
Beyond stenosis and transplant monitoring, renal Doppler provides valuable information about overall kidney perfusion. The resistive index measured in the intrarenal arteries reflects the health of the small blood vessels within the kidney. An elevated resistive index (above 0.7) may indicate kidney damage from conditions such as diabetic nephropathy, chronic kidney disease, or hypertensive kidney injury.
Renal Vein Thrombosis
Renal Doppler can detect blood clots in the renal veins, a condition known as renal vein thrombosis. This condition can cause sudden flank pain, blood in the urine, and rapid kidney function decline. It is more common in patients with nephrotic syndrome, certain cancers, or clotting disorders. Doppler identifies the clot by demonstrating absent or reversed flow in the affected renal vein.
Who Needs a Renal Doppler Ultrasound?
Renal Doppler is not a routine screening test for everyone. It is specifically indicated for patients with certain clinical findings or risk factors. Your doctor may recommend a renal Doppler if you have:
- Resistant hypertension: High blood pressure that does not respond adequately to three or more medications
- Sudden onset of high blood pressure, especially in young adults (under 30) or older adults (over 55)
- Unexplained decline in kidney function, particularly if it worsens after starting ACE inhibitor or ARB medications
- An abdominal bruit (unusual sound heard by stethoscope over the kidney area)
- History of kidney transplant, particularly if there is a change in kidney function or blood pressure
- Recurrent episodes of flash pulmonary edema (sudden fluid in the lungs) without a clear cardiac cause
- Asymmetric kidney size discovered on other imaging studies (one kidney smaller than the other)
- Suspected renal vein thrombosis with symptoms of flank pain, blood in urine, and protein in urine
- Diabetes with worsening kidney function, to assess for both large and small vessel kidney disease
Need a Renal Doppler Assessment?
At Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center in Dubai Healthcare City, we provide expert renal Doppler ultrasound for kidney blood flow assessment, renal artery stenosis screening, and transplant monitoring.
The Connection Between Renal Artery Stenosis and Hypertension
Renal artery stenosis is responsible for approximately 1-5% of all hypertension cases and a significant percentage of resistant hypertension cases. When one or both renal arteries narrow, the affected kidney perceives reduced blood flow and activates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which raises blood pressure throughout the body.
This creates a cycle where the body raises blood pressure to force more blood through the narrowed artery, but the high pressure damages blood vessels throughout the body. Detecting RAS through renal Doppler allows physicians to address the root cause of hypertension rather than just treating the elevated numbers with more medications. Treatment options may include angioplasty with stenting or medical management depending on the severity and cause of stenosis.
Renal Doppler in the Dubai Context
Several factors specific to the UAE population make renal Doppler particularly relevant for residents of Dubai:
- High diabetes prevalence: The UAE has one of the highest diabetes rates globally, and diabetic nephropathy is a leading cause of kidney failure. Renal Doppler helps assess vascular changes in diabetic kidneys before significant damage occurs.
- Hypertension burden: Hypertension affects a large segment of the UAE population, and screening for secondary causes like RAS is essential for patients with difficult-to-control blood pressure.
- Active transplant programs: The UAE has growing kidney transplant programs, and renal Doppler is essential for post-transplant vascular monitoring.
- Diverse expatriate population: Dubai's multicultural population includes individuals from regions with varying prevalence of kidney disease risk factors, making individualized screening important.
- Heat-related dehydration: Chronic dehydration in hot climates can contribute to kidney stress and may accelerate existing kidney conditions, warranting closer monitoring in susceptible patients.
Renal Doppler vs CT Angiography vs MR Angiography
Several imaging methods can evaluate the renal arteries. The table below compares Renal Doppler with CT Angiography and MR Angiography to help patients and physicians understand the strengths and trade-offs of each approach.
| Feature | Renal Doppler Ultrasound | CT Angiography (CTA) | MR Angiography (MRA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiation | None | Yes (ionizing radiation) | None |
| Contrast dye | Not required | Iodinated contrast (IV) | Gadolinium contrast (IV) |
| Sensitivity for RAS | 85% – 95% | 95% – 100% | 90% – 100% |
| Best for | Screening, transplant follow-up, serial monitoring | Definitive pre-surgical mapping | Patients who cannot receive iodinated contrast |
| Kidney function concern | Safe regardless of kidney function | Contrast may worsen kidney disease | Gadolinium risk in severe kidney disease |
| Scan duration | 20 – 30 minutes | 5 – 10 minutes | 30 – 45 minutes |
| Repeatability | Unlimited, no cumulative risk | Limited by radiation and contrast load | Limited by contrast and availability |
| Cost (AED, approximate) | 600 – 1,200 | 1,500 – 3,000 | 2,500 – 5,000 |
Renal Doppler is the preferred first-line test. CTA and MRA are typically reserved for cases requiring more detailed anatomical mapping or when Doppler results are inconclusive.
How to Prepare for a Renal Doppler Ultrasound
Renal Doppler is one of the few Doppler types that requires fasting before the scan. Proper preparation for your Doppler ultrasound ensures the best possible image quality and accurate results.
- Fast for 6 to 8 hours before your appointment. Water may be allowed in small amounts; confirm with your clinic.
- Avoid gas-producing foods the day before (beans, lentils, carbonated drinks, raw vegetables).
- Continue all regular medications with a small sip of water unless instructed otherwise.
- Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing, ideally a two-piece outfit for easy abdominal access.
- Bring your referral, insurance card, and any previous kidney imaging reports or blood test results.
What Happens During the Scan
During a renal Doppler ultrasound, you lie on your back on an examination table. The sonographer applies warm gel to your abdomen and places a transducer over the kidney area. The transducer sends and receives sound waves that create real-time images of the kidneys and their blood vessels on a monitor.
You may be asked to lie on your side, take deep breaths, or hold your breath at various points during the scan. These position changes help the sonographer obtain optimal views of the renal arteries, which can be challenging to visualize due to their depth and the presence of bowel gas. The entire scan typically takes 20 to 30 minutes.
A radiologist reviews the images and measurements after the scan and provides a detailed report to your referring physician. Results are usually available within 24 hours.
Renal Doppler at DCDC Dubai Healthcare City
At Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center, we provide comprehensive renal Doppler ultrasound services performed by experienced radiologists using advanced Doppler ultrasound equipment. Our team has extensive experience in evaluating native and transplanted kidneys, with detailed reporting that helps nephrologists and internists make well-informed treatment decisions.
Located in Dubai Healthcare City, we serve patients referred by nephrologists, internists, cardiologists, and transplant teams across Dubai. We accept most major insurance plans and offer transparent self-pay options for uninsured patients.
Need a Renal Doppler Ultrasound?
At Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center in Dubai Healthcare City, we provide expert renal Doppler ultrasound services for kidney blood flow assessment, renal artery stenosis screening, and transplant monitoring.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Final Thoughts
Renal Doppler ultrasound is an invaluable diagnostic tool that provides information about kidney vascular health that no other non-invasive test can match. From detecting renal artery stenosis as a cause of resistant hypertension to monitoring transplanted kidneys for vascular complications, this test plays a critical role in kidney care. Its safety, accessibility, and ability to be repeated without risk make it a cornerstone of renal diagnostics.
For residents of Dubai, where diabetes and hypertension are prevalent, renal Doppler offers a proactive way to assess kidney vascular health before irreversible damage occurs. For pricing details, see our guide on Doppler ultrasound cost in Dubai. At Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center in Dubai Healthcare City, our experienced radiology team provides thorough renal Doppler assessments with clear, actionable reports that support your kidney health journey.
Источники и ссылки
Эта статья проверена нашей медицинской командой и ссылается на следующие источники:
- American College of Radiology - Renal Artery Stenosis Imaging Guidelines
- National Kidney Foundation - Renal Vascular Disease
- European Society of Radiology - Renal Doppler Standards
- Transplantation Society - Post-Transplant Monitoring Guidelines
Медицинский контент на этом сайте проверяется врачами, лицензированными DHA. См. нашу редакционную политику для получения дополнительной информации.