Points cles
- Doppler ultrasound is the gold standard first-line test for detecting deep vein thrombosis, offering real-time visualization of blood clots in leg veins without radiation
- Common DVT symptoms include sudden leg swelling, pain or tenderness in the calf, warmth, and redness, though some DVTs produce no symptoms at all
- The compression ultrasound technique, where the probe presses on the vein, is over 95% accurate for detecting DVT in the thigh and behind the knee
- Dubai residents face specific DVT risk factors including long-haul flights, sedentary office work, and dehydration from the hot climate
- If DVT is detected, prompt anticoagulation therapy is essential to prevent the clot from growing or breaking off and traveling to the lungs as a pulmonary embolism
A Doppler ultrasound for DVT is a non-invasive imaging test that uses sound waves to detect blood clots in the deep veins of your legs. Deep vein thrombosis, or DVT, occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, most commonly in the lower leg or thigh. Left untreated, a DVT can break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a potentially fatal pulmonary embolism. Doppler ultrasound is the first-line diagnostic tool for this condition, providing rapid, accurate, and radiation-free results.
DVT affects an estimated 1 to 2 people per 1,000 annually worldwide, and its incidence is rising due to increasingly sedentary lifestyles and aging populations. For Dubai residents, additional factors such as frequent long-distance travel, prolonged office hours, and heat-related dehydration further elevate the risk. This comprehensive guide explains how Doppler ultrasound detects DVT, what symptoms should prompt testing, how accurate the test is, and what to expect if a clot is found.
How Doppler Ultrasound Detects Blood Clots in Deep Veins
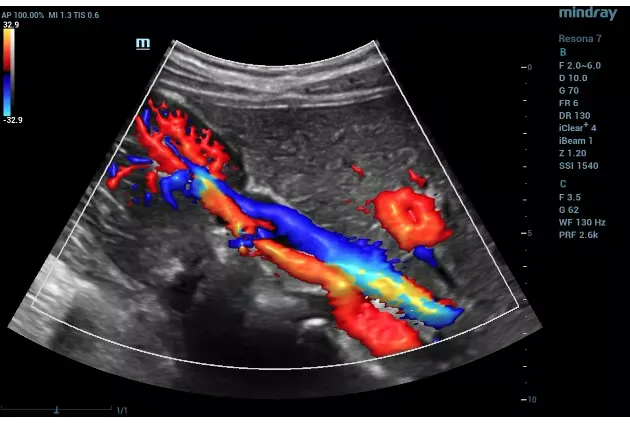
Doppler ultrasound works by emitting high-frequency sound waves that bounce off red blood cells as they move through your veins. The returning echoes are converted into images and color-coded flow maps that allow the radiologist to see exactly where blood is flowing normally and where it may be obstructed. When a blood clot is present in a deep vein, the Doppler signal will show absent or reduced flow at that location.
The test combines two complementary techniques. B-mode ultrasound produces a grayscale image of the vein structure, showing the vein walls and any visible clot material within them. Color Doppler overlays a color map onto this image, with different colors representing blood flowing toward and away from the probe. Spectral Doppler provides a waveform that shows the speed and direction of blood flow at any specific point, revealing subtle flow disturbances that may indicate a partial clot.
Together, these techniques give the radiologist a comprehensive view of your venous system, allowing detection of both complete and partial blockages with high accuracy. The examination is performed in real time, meaning the radiologist can evaluate the veins dynamically as you breathe and as the probe is positioned at different angles.
"When a patient presents with sudden leg swelling, every minute counts. DVT Doppler is the fastest path to a definitive answer," says Dr. Osama Elzamzami, Consultant Radiologist at DCDC. "The compression test is elegantly simple, a normal vein collapses under gentle pressure while a clot-filled vein does not, and in experienced hands it provides over 95% accuracy for proximal DVT. I always emphasize to patients that this test could be the single decision that prevents a pulmonary embolism."
Symptoms That Trigger DVT Testing
DVT does not always cause obvious symptoms, which makes it particularly dangerous. However, when symptoms do appear, they typically affect one leg and develop relatively quickly. Recognizing these warning signs and seeking prompt medical evaluation can be life-saving.
- Sudden swelling in one leg, especially if it develops over hours to days rather than gradually over weeks
- Pain or tenderness in the calf or thigh that may feel like a cramp or deep ache, often worsening when standing or walking
- Warmth over the affected area, noticeable when touching one leg compared to the other
- Redness or discoloration of the skin, ranging from a subtle pinkish hue to a more obvious reddish-blue color
- Visible swelling of superficial veins near the surface of the skin
- A feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected leg
It is important to understand that DVT can also be completely silent. Some patients discover they have DVT only when they develop symptoms of pulmonary embolism, such as sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid heartbeat, or coughing up blood. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention.
Doctors use clinical assessment tools such as the Wells Score to estimate the probability of DVT before ordering a Doppler ultrasound. This scoring system considers factors like recent surgery, cancer history, leg swelling, tenderness, immobilization, and whether an alternative diagnosis is equally likely. A high Wells Score strongly supports the need for urgent ultrasound evaluation.
The Compression Ultrasound Technique
The most critical component of a DVT ultrasound examination is the compression test. This simple yet highly effective technique is what makes ultrasound so reliable for detecting blood clots in the veins.
During the compression test, the sonographer places the ultrasound probe directly over a vein and applies gentle downward pressure. A normal, clot-free vein will collapse completely under this pressure because veins are thin-walled and flexible. However, if a blood clot is present inside the vein, the vein will not compress fully. The clot acts as a solid mass that prevents the vein walls from coming together. This non-compressibility is the single most important sign of DVT on ultrasound.
The sonographer systematically performs compression at multiple points along the deep veins of the leg, typically starting at the common femoral vein in the groin and working downward through the superficial femoral vein, the popliteal vein behind the knee, and in many cases the calf veins as well. At each point, the vein is assessed both with and without compression, and the Doppler signal is evaluated for normal flow patterns.
A complete DVT ultrasound examination of one leg typically takes 15 to 30 minutes, depending on the complexity of the case. In some situations, both legs are examined for comparison or to check for bilateral DVT, which can extend the examination time.
Accuracy of Doppler Ultrasound vs. Other DVT Tests
Doppler ultrasound is the established first-line test for DVT because of its excellent combination of accuracy, availability, safety, and cost-effectiveness. However, it is useful to understand how it compares to other diagnostic methods.
| Test | Sensitivity | Specificity | Key Advantages | Key Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Ultrasound (proximal DVT) | 95% – 99% | 95% – 99% | No radiation, portable, real-time, repeatable | Operator dependent; calf veins harder to assess |
| D-dimer Blood Test | 95% – 97% | 40% – 60% | Very high negative predictive value; rules out DVT | Low specificity; elevated in many conditions (infection, surgery, pregnancy) |
| CT Venography | 95% – 100% | 95% – 100% | Excellent for pelvic and abdominal veins | Radiation exposure, IV contrast required, higher cost |
| MR Venography | 92% – 100% | 95% – 100% | No radiation, good for pelvic veins | Expensive, longer scan time, limited availability |
Sensitivity and specificity values are approximate and based on published clinical studies. Actual performance depends on the anatomical location and the operator's experience.
In clinical practice, the diagnostic pathway usually begins with a clinical assessment (Wells Score) combined with a D-dimer blood test. If the D-dimer is negative and the clinical probability is low, DVT can often be ruled out without imaging. However, if the D-dimer is elevated or the clinical suspicion is moderate to high, a Doppler ultrasound is performed. CT venography is typically reserved for cases where ultrasound results are inconclusive, or when DVT in the pelvic or abdominal veins is suspected.
One important consideration is that ultrasound is somewhat less sensitive for isolated calf vein DVT compared to proximal DVT in the thigh. If clinical suspicion remains high after a negative ultrasound, a repeat scan may be recommended in 5 to 7 days to check for clot propagation from the calf into the proximal veins.
Suspect DVT? Get Tested Today
At Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center in Dubai Healthcare City, our experienced radiologists perform DVT Doppler ultrasound with same-day results. No radiation, no special preparation needed.
DVT Risk Factors and Dubai-Specific Risks
Understanding who is at risk for DVT is essential for prevention and early detection. While anyone can develop a blood clot, certain factors significantly increase the likelihood. Dubai residents and the broader UAE population face several risk factors that deserve particular attention.
Long-Haul Air Travel
Dubai is a major international travel hub, and many residents regularly take long-haul flights exceeding 4 hours. Prolonged immobility in a cramped airline seat restricts blood flow in the legs, and the lower cabin pressure and reduced humidity contribute to dehydration and blood thickening. The risk of DVT is approximately two to three times higher after flights lasting more than 4 hours. Frequent flyers who travel long distances multiple times per year face a cumulative risk that is often underestimated.
Sedentary Office Work
The modern corporate lifestyle in Dubai often involves sitting at a desk for 8 to 10 hours or more per day. Prolonged sitting, whether at work or during long drives in traffic, reduces blood flow velocity in the leg veins and creates conditions favorable for clot formation. The combination of an air-conditioned indoor environment and lack of movement is a significant but underappreciated risk factor.
Heat and Dehydration
Dubai's extreme summer temperatures, which regularly exceed 45 degrees Celsius, cause significant fluid loss through sweating. Dehydration concentrates the blood and makes it more prone to clotting. Many residents do not drink enough water, particularly during Ramadan fasting hours or when spending time outdoors during the hotter months. This chronic mild dehydration is a risk factor that is unique to the regional climate.
Other Established Risk Factors
- Recent surgery or hospitalization, especially orthopedic procedures involving the hip or knee
- Active cancer or cancer treatment, which increases blood clotting tendency
- Pregnancy and the postpartum period, due to hormonal changes and compression of pelvic veins
- Oral contraceptive pills or hormone replacement therapy containing estrogen
- Obesity, which increases pressure on pelvic and leg veins and promotes inflammation
- Family or personal history of DVT or pulmonary embolism
- Inherited clotting disorders such as Factor V Leiden or prothrombin gene mutation
- Age over 60, as clotting risk increases with advancing age
- Smoking, which damages blood vessel walls and promotes clot formation
What Happens If DVT Is Found?
When a Doppler ultrasound confirms the presence of DVT, treatment typically begins immediately. The primary goal is to prevent the clot from growing larger, prevent it from breaking off and causing a pulmonary embolism, and reduce the risk of long-term complications such as post-thrombotic syndrome.
Anticoagulation Therapy
The cornerstone of DVT treatment is anticoagulation, commonly known as blood-thinning medication. These drugs do not dissolve existing clots but prevent new clots from forming and stop the existing clot from growing. The body's own fibrinolytic system then gradually breaks down the clot over weeks to months. Modern treatment typically involves direct oral anticoagulants such as rivaroxaban or apixaban, which do not require regular blood monitoring. Treatment duration ranges from 3 months for a first episode with a clear temporary cause to indefinite therapy for recurrent or unprovoked DVT.
Compression Stockings and Follow-Up
Graduated compression stockings apply gentle pressure to the legs, helping blood flow back toward the heart and reducing swelling. They are often recommended for at least two years after a DVT diagnosis to reduce the risk of post-thrombotic syndrome. Repeat Doppler ultrasound examinations are typically performed during and after treatment to monitor clot resolution, with a baseline scan at the time of diagnosis followed by scans at 3 to 6 months to track the response to therapy.
Advanced Interventions
In severe cases, such as massive iliofemoral DVT that threatens limb viability, more aggressive treatments may be considered. These include catheter-directed thrombolysis (delivering clot-dissolving drugs directly to the clot), mechanical thrombectomy (physically removing the clot), or placement of an inferior vena cava filter in patients who cannot take anticoagulants. These interventions are reserved for specific clinical situations and are performed at specialized vascular centers.
Prevention Strategies for Dubai Residents
Prevention is always preferable to treatment when it comes to DVT. Dubai residents can take several practical steps to reduce their risk, particularly given the lifestyle and environmental factors in the region.
- Stay well hydrated by drinking at least 2 to 3 liters of water daily, increasing intake during summer months and when fasting
- Take regular movement breaks every 60 to 90 minutes during long periods of sitting at work; simple calf raises and ankle circles promote venous return
- During long flights, stand up and walk the cabin every 1 to 2 hours, perform seated leg exercises, and wear compression socks if you have risk factors
- Maintain a healthy weight through regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week
- If you take oral contraceptives or hormone therapy, discuss DVT risk with your doctor, especially before long travel
- After surgery or illness requiring bed rest, follow your doctor's instructions regarding early mobilization and preventive blood thinners
- Avoid crossing your legs for prolonged periods, as this compresses veins and restricts blood flow
- If you have a personal or family history of blood clots, ask your doctor about screening for inherited clotting disorders
DVT Doppler Ultrasound at DCDC Dubai
At Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center in Dubai Healthcare City, DVT Doppler ultrasound is performed by experienced radiologists using advanced Doppler ultrasound equipment that provides high-resolution B-mode imaging and sensitive color and spectral Doppler capabilities. The clinic follows standardized compression ultrasound protocols to ensure thorough and accurate evaluation of the deep venous system.
Results are typically available the same day, with detailed reports that include the location and extent of any clot found, the degree of venous obstruction, and recommendations for follow-up. Close coordination with referring physicians, including internists, vascular surgeons, and hematologists, ensures that patients receive appropriate and timely treatment when DVT is confirmed.
With over 1,000 diagnostic scans performed every month and more than 13 years of continuous operation since 2013, DCDC has built a reputation as one of the leading diagnostic centers in Dubai Healthcare City. The center's multilingual team serves patients from across the UAE and internationally, ensuring clear communication and patient-centered care throughout every examination.
A recent case highlights the importance of timely DVT screening: a 45-year-old marketing executive from Dubai visited DCDC after noticing progressive swelling and tightness in her left calf following a 14-hour business flight from London. She initially thought it was just travel fatigue, but when the swelling persisted for two days, her GP urgently referred her for a venous Doppler. The compression ultrasound revealed an acute DVT in the left popliteal vein extending into the distal superficial femoral vein. She was started on anticoagulation therapy the same afternoon. At her three-month follow-up Doppler, the clot had largely resolved with no signs of post-thrombotic syndrome, an outcome her hematologist attributed directly to the early detection and rapid treatment initiation.
Worried About DVT Symptoms?
A DVT Doppler ultrasound at Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center in Dubai Healthcare City can quickly and accurately check your leg veins for blood clots. Same-day results. No radiation. No special preparation needed.
Questions frequentes
Final Thoughts
Deep vein thrombosis is a common but potentially life-threatening condition that can be detected quickly and accurately with Doppler ultrasound. The compression ultrasound technique is the diagnostic standard for a reason: it is safe, highly accurate for proximal DVT, requires no radiation or contrast dye, and provides immediate results. For anyone experiencing sudden leg swelling, pain, or warmth, a DVT Doppler ultrasound should be performed promptly to rule out or confirm a blood clot.
Dubai residents face a unique combination of DVT risk factors, from frequent long-haul travel and sedentary office lifestyles to heat-induced dehydration. Awareness of these risks, combined with simple preventive measures and timely testing when symptoms arise, can prevent serious complications including pulmonary embolism. For pricing details, see our guide on Doppler ultrasound cost in Dubai. If you are concerned about DVT or have risk factors, do not delay. Book a Doppler ultrasound at Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center in Dubai Healthcare City for peace of mind and prompt, expert evaluation.
Sources et references
Cet article a ete revise par notre equipe medicale et fait reference aux sources suivantes :
- American College of Chest Physicians - Antithrombotic Therapy Guidelines
- Society for Vascular Surgery - DVT Diagnosis and Management
- Radiological Society of North America - Venous Ultrasound
- American Heart Association - Venous Thromboembolism
- European Society of Cardiology - VTE Guidelines
Le contenu medical de ce site est revise par des medecins agrees DHA. Voir notre politique editoriale pour plus d'informations.