Key Takeaways
- A CT angiogram (CTA) is a non-invasive imaging test that uses CT technology and contrast dye to visualize blood vessels and the heart
- Cardiac CT angiography can detect coronary artery disease, blockages, and plaque buildup without catheterization
- The scan takes approximately 10-15 minutes and requires no hospital admission or recovery time
- CT coronary angiography is particularly useful for intermediate-risk patients and those with atypical chest pain
- DCDC uses advanced multi-slice CT technology for high-resolution cardiac imaging in Dubai Healthcare City
A CT angiogram, also known as CT angiography (CTA), is an advanced medical imaging test that combines computed tomography with a special contrast dye to produce detailed images of blood vessels throughout the body. When focused on the heart, it is called cardiac CT angiography or CT coronary angiography (CTCA), and it allows doctors to evaluate the coronary arteries for narrowing, blockages, or plaque buildup without inserting a catheter.
This comprehensive guide explains what a CT angiogram is, how it works, who should consider having one, the advantages over traditional catheter-based angiography, and what to expect at Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center in Dubai Healthcare City.
What Does a CT Angiogram Show?
A CT angiogram produces highly detailed, three-dimensional images of blood vessels and surrounding tissues. When used for cardiac assessment, a CTCA scan specifically shows the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. The images reveal whether these arteries are narrowed, blocked, or contain calcified or soft plaque deposits that could lead to a heart attack.
Beyond the coronary arteries, cardiac CT angiography can also evaluate the heart chambers, heart valves, the aorta, and the pulmonary arteries. This makes it a versatile diagnostic tool that provides a comprehensive view of cardiovascular health in a single examination.
- Coronary artery narrowing or stenosis
- Calcified and non-calcified plaque deposits
- Coronary artery anomalies or anatomical variations
- Bypass graft patency in post-surgical patients
- Aortic aneurysm or dissection
- Pulmonary embolism when scanning chest vessels
- Structural heart abnormalities and valve conditions
How Does a CT Angiogram Work?
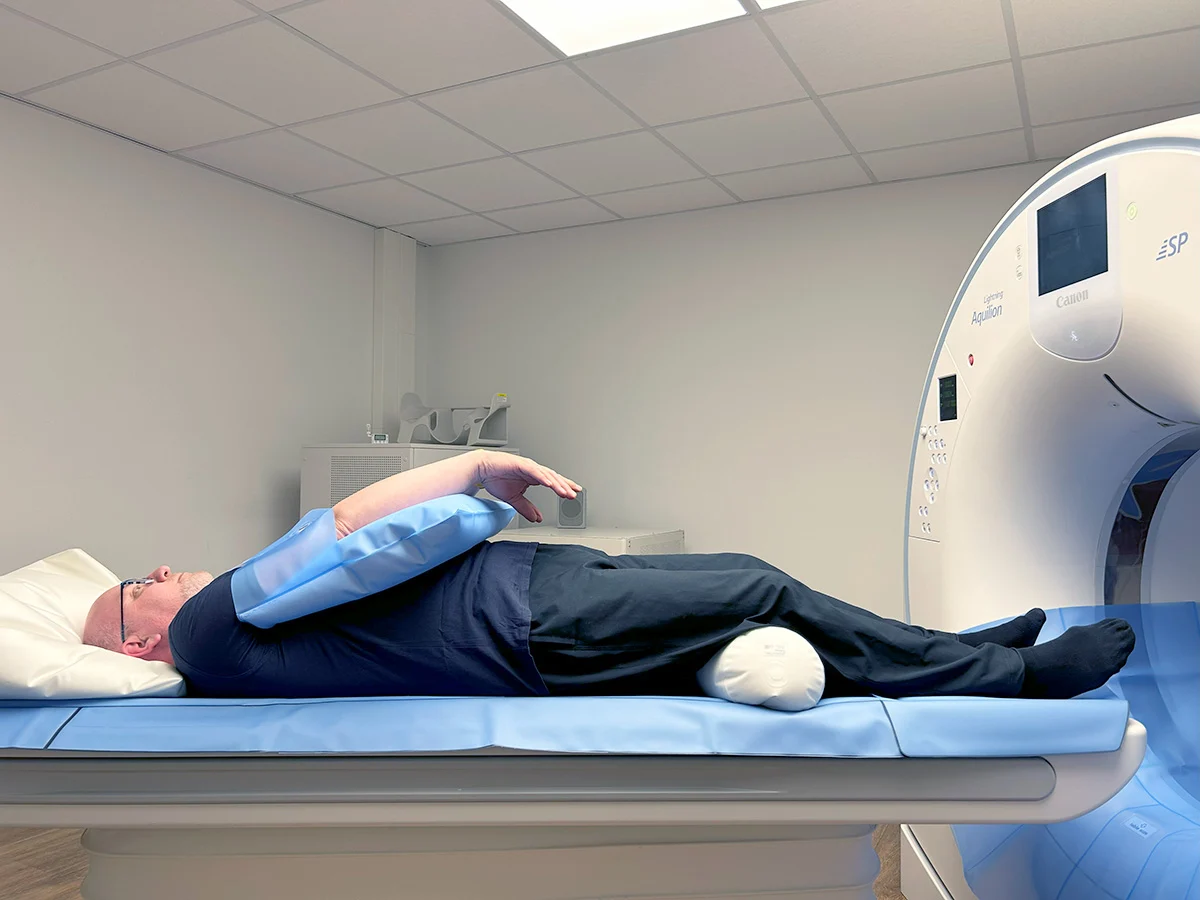
A CT angiogram works by combining a standard CT scanner with an intravenous contrast agent (iodine-based dye). The patient lies on a motorized table that passes through a doughnut-shaped CT scanner. As the scanner rotates rapidly around the body, it takes hundreds of cross-sectional X-ray images in just a few seconds. Meanwhile, the contrast dye flows through the bloodstream, making the blood vessels appear bright and clearly defined on the images.
Modern multi-slice CT scanners, like those used at DCDC, can capture images of the heart between heartbeats using ECG-gated technology. This synchronization eliminates motion blur caused by the beating heart, producing crisp images of even the smallest coronary artery branches. Advanced software then reconstructs these images into detailed 3D models that cardiologists and radiologists can examine from any angle.
"The CT angiogram has transformed how we approach early detection of coronary artery disease," says Dr. Shahoo Mazhari, Consultant Cardiologist at DCDC. "For patients who fall in the intermediate-risk category, it gives us a clear, non-invasive window into their coronary health without any of the risks of catheterization."
Who Needs a CT Angiogram?
Not everyone with heart-related concerns requires a CT angiogram. Doctors typically recommend cardiac CT angiography for patients who fall into specific clinical categories where the test provides the most diagnostic value.
Patients with Intermediate Risk of Coronary Artery Disease
The greatest benefit of CT coronary angiography is seen in patients with an intermediate risk of coronary artery disease. These are individuals who have some risk factors such as high cholesterol, family history, smoking history, or diabetes but whose symptoms are not severe enough to warrant immediate invasive angiography. For this group, a CTCA scan can either rule out significant disease or identify issues that require further treatment.
Atypical Chest Pain
Patients experiencing chest pain that is not clearly cardiac in origin benefit from CT angiography because the test can quickly and accurately determine whether coronary artery disease is responsible. If the arteries appear normal, doctors can focus on other potential causes of pain, saving the patient from unnecessary invasive procedures.
Inconclusive Stress Test Results
When a treadmill stress test or nuclear stress test produces borderline or inconclusive results, a CT angiogram provides a direct anatomical view of the coronary arteries. This helps clarify whether there is a genuine blockage or whether the stress test result was a false positive.
Pre-Surgical Planning and Post-Bypass Evaluation
Cardiac surgeons may request a CT angiogram before certain heart procedures to map out coronary artery anatomy. It is also used to evaluate bypass grafts in patients who have previously undergone coronary artery bypass surgery, checking whether the grafts remain open and functioning properly.
CT Angiogram vs Traditional Angiogram: Key Differences
One of the most common questions patients ask is how a CT angiogram compares to a traditional catheter-based angiogram. Both tests evaluate the coronary arteries, but they differ significantly in terms of invasiveness, risk, recovery, and cost. Understanding these differences helps patients make informed decisions in consultation with their cardiologist.
| Feature | CT Angiogram | Traditional (Catheter) Angiogram |
|---|---|---|
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive (IV contrast only) | Invasive (catheter inserted through artery) |
| Duration | 10-15 minutes | 30-60 minutes |
| Recovery | No downtime, resume normal activities | 4-6 hours rest, wound care required |
| Radiation | Low dose with modern CT scanners | Higher fluoroscopy radiation exposure |
| Intervention capability | Diagnostic only | Can place stent during same procedure |
| Best suited for | Intermediate risk, screening, ruling out CAD | High risk, confirmed disease, planned intervention |
For a detailed comparison, see our article on CT angiogram vs traditional angiogram.
The key advantage of a CT angiogram is that it provides reliable diagnostic information without the risks associated with arterial catheterization. However, if a significant blockage is found on CT angiography, the patient may still need a traditional angiogram to place a stent or plan surgery. For a more in-depth comparison, read our dedicated guide on CT angiogram vs traditional angiogram.
Advantages of CT Coronary Angiography
CT coronary angiography has become increasingly popular in cardiology because it offers several important advantages over other diagnostic methods. As scanner technology has improved, the accuracy and reliability of cardiac CT have reached levels that rival invasive angiography for many clinical scenarios.
- Non-invasive: No arterial catheterization, no groin puncture, and no sedation required
- Fast results: The scan itself takes 10-15 minutes, with results typically available the same day or within 24 hours
- High negative predictive value: A normal CT angiogram is extremely reliable at ruling out significant coronary artery disease
- Outpatient procedure: No hospital admission or overnight stay needed
- Comprehensive evaluation: Assesses coronary arteries, heart structure, aorta, and pulmonary vessels simultaneously
- Lower complication rate: Significantly fewer risks compared to invasive catheter angiography
Limitations and Considerations
While CT angiography is a powerful diagnostic tool, it is not appropriate for every patient. Heavy coronary calcification can sometimes make it difficult to assess the degree of narrowing accurately. Patients with irregular heart rhythms (atrial fibrillation) may produce motion artifacts that reduce image quality, although modern scanners with high temporal resolution have significantly reduced this issue.
Additionally, CT angiography uses iodine-based contrast dye, which is not suitable for patients with severe kidney disease or known iodine allergies. Patients with very high heart rates may need beta-blocker medication before the scan to slow their heart rate and improve image quality. Your cardiologist will evaluate whether CT angiography is the right choice based on your individual health profile.
The Role of Calcium Score in CT Cardiac Assessment
A closely related test is the coronary calcium score test, which is often performed alongside or before a CT angiogram. The calcium score measures the amount of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries using a low-dose CT scan without contrast dye. A high calcium score suggests increased risk of coronary artery disease and may prompt the doctor to recommend a full CT angiogram for more detailed evaluation.
Together, the calcium score and CT angiogram provide a comprehensive picture of coronary artery health. The calcium score quantifies overall plaque burden, while the CT angiogram reveals the exact location and severity of any blockages.
CT Angiogram Technology at DCDC Dubai Healthcare City
At Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center, cardiac CT angiography is performed using advanced multi-slice CT scanner technology that delivers high-resolution images with reduced radiation exposure. The center's radiology team works closely with consultant cardiologists to ensure each scan is tailored to the patient's clinical needs.
With over 13 years of operation in Dubai Healthcare City and more than 1,000 diagnostic scans performed every month, DCDC has established itself as a leading diagnostic center in Dubai. The center attracts international patients from around the world who seek premier cardiac imaging services, alongside residents from across the UAE.
DCDC's cardiac imaging workflow includes pre-scan heart rate optimization, ECG-gated image acquisition, and advanced 3D reconstruction software. This approach ensures that patients receive accurate, clinically actionable results. Located in Dubai Healthcare City, the center serves patients from across Dubai, including Oud Metha, Karama, Bur Dubai, and the wider UAE.
One patient who benefited from this approach was a 58-year-old CEO visiting from Saudi Arabia who had been experiencing occasional chest tightness during business travel. Rather than dismissing the symptom, he visited DCDC for a comprehensive cardiac evaluation. His CT angiogram revealed mild stenosis in one of his coronary arteries, an early finding that would have been missed by a standard stress test. "Catching mild stenosis at this stage is exactly what preventive cardiology is about," explains Dr. Shahoo Mazhari, Consultant Cardiologist at DCDC. "We were able to start him on targeted medical therapy and lifestyle modifications before the narrowing progressed to something more serious." The patient returned home with a clear treatment plan and peace of mind.
To learn more about what happens during the examination, read our step-by-step guide on the CT angiogram procedure.
Book a CT Angiogram at DCDC
At Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center in Dubai Healthcare City, our cardiology and radiology teams provide expert CT coronary angiography using advanced multi-slice CT technology. Get accurate cardiac imaging with fast results and personalized care.
Book CT AngiogramFrequently Asked Questions
Final Thoughts
A CT angiogram is one of the most valuable non-invasive tools available for evaluating coronary artery health and detecting cardiovascular disease early. For patients at intermediate risk or those with atypical symptoms, cardiac CT angiography provides reliable answers without the risks and recovery time associated with invasive catheterization. At Doctors Clinic Diagnostic Center, patients benefit from advanced CT technology, experienced specialists, and a patient-centered approach to cardiac imaging.
Understanding what a CT angiogram is, what it can detect, and when it is appropriate empowers you to have informed conversations with your cardiologist. If you have been advised to undergo cardiac imaging or have risk factors for heart disease, discussing CT coronary angiography with your doctor is a practical first step toward protecting your heart health. For details on pricing and insurance coverage, see our guide on CT angiogram cost in Dubai.
Sources & References
This article was reviewed by our medical team and references the following sources:
- American Heart Association - Coronary CT Angiography
- Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography (SCCT) Guidelines
- European Society of Cardiology - Cardiac Imaging Guidelines
- American College of Radiology - CT Angiography Appropriateness Criteria
Medical content on this site is reviewed by DHA-licensed physicians. See our editorial policy for more information.